Pipe cooling method using heat pipe: Simple method to prevent crack in mass concrete caused by hydration heat
TEKKEN CORPORATION
Outline
Reduction of initial defects of concrete is required for a concrete structure these days, with the object of improving durability. In particular, cracking due to hydration heat of cement is becoming a problem for the case of mass concrete. Pipe cooling method, by which cooled water circulates inside pipes, is generally used as a method for suppressing temperature of the mass concrete. However, this method requires a large space for a device that controls circulation of water, a large quantity of water, and complicated electric equipment for piping and therefore has problems in both workability and economic efficiency. Against this backdrop, development of a method which can suppress rise of temperature by use of simple equipment has been desired. Therefore, another pipe cooling method using a heat pipe was invented: By this method, a heat pipe, which is capable of transferring a large amount of heat of the concrete, is installed in the concrete to suppresses rise of temperature due to hydration heat of concrete without using complicated equipment, a large device, and/or a large quantity of water. Since the heat pipe transfers heat where there is temperature difference, this technology contributes to both decarbonization and reduction of greenhouse gas emission.
Description
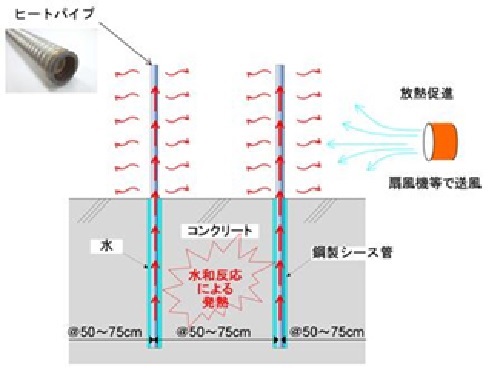
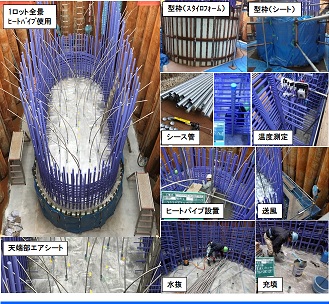
This is a very simple method of inserting a heat pipe in a steel sheath pipe buried in advance to release the heat inside the concrete to the air. Moreover, when a protruding portion of the heat pipe is cooled by a fan to increase thermal transfer ability, heat dissipation can be enhanced to obtain higher cooling effect. Most significant characteristics of this method is that instead of utilizing circulation of cooling water or water temperature control device of the existing technology, the heat pipe is used to suppress rise of temperature of the concrete naturally, without using electric power, by the heat transfer which is caused by the difference in temperature between inside and outside of the concrete (refer to Fig. 1,2) This is the first time in Japan that the heat pipe is utilized for suppression of rise of temperature of the cast concrete.
This method also has following characteristics:
[Economic efficiency] Cost can be significantly reduced as the heat pipe can be reused. Moreover, construction cost can also be reduced in a site where concrete is cast several times and places. *The heat pipe can be reused on such occasions.
[Plant is not required] Plant equipment for control of cooling water circulation/temperature is not required. Therefore, this method can be applied to a site where water cannot be easily procured.
[Easy to construct] This is a simple method that only heat pipe installation is required. Troublesome construction management such as water temperature control is not necessary.
Other Innovation Challenges
Recycling green resources: Development of new way of biomass gas power generation
TEKKEN CORPORATION
Similar Innovation Challenges
Achieving net zero carbon emissions from paint finishing processes
Taikisha Ltd.
Activities for reducing GHG of business operations in Nissin Electric Group
Nissin Electric Co., Ltd.


-1人工光合成技術.jpg?id=2&tid=759&imageNumber=1)