Reusing Coal Ash as Civil Engineering Material Through CO₂ Absorbing Technology Using Microwave Irradiation
The Chugoku Electric Power Company, Incorporated
Outline
We have been engaged in developing "Triple C recycling technology (CO₂-TriCOM)", a new technology in which the coal ash and CO₂ gas generated in a thermal power station are mixed with the concrete powder from electric pole waste material, which is a byproduct of the electric power business, and are irradiated with microwaves to absorb CO₂ in the sintered material. This is the first technology using microwaves to absorb CO₂ in Japan. If a light sintered material about the same size as sand can be manufactured by the same heating principle as a microwave oven, it could be available for greening base material and light-weight embankment material as a civil engineering material with the property of being more permeable and more light-weight than sand. We will contribute to preventing global warming through the practical application of this technology.
Description
As part of our efforts to solve environmental issues in coal-fired thermal power generation such as CO₂ emissions and the generation of coal ash, we are engaged in developing the "Triple C Recycling Technology" (commonly called "CO₂-TriCOM"), which allows for CO₂, coal ash, and the like to be reused as material for civil engineering work.
"CO₂-TriCOM" is technology which mixes not only CO₂ gas and coal ash but also electric pole waste material, which is a byproduct of the electric power business. The mixture is sintered by heating using microwaves, and during this process, the concrete powder (CaO) absorbs CO₂ and absorbs it as carbonate. If a sintered material with a grain size similar to that of sand can be manufactured, it could be available for greening base material and light-weight embankment material as a civil engineering material with the property of being more permeable and more light-weight than sand. "CO₂-TriCOM" is a revolutionary carbon recycling technology which "absorbs" CO₂ in coal ash and electric pole waste material, which conventionally presented an issue as waste, and makes them reborn as a new product. Provisional calculations indicate that approximately 60 kilograms of CO₂ can be absorbed per ton of sintered material.
To promote our further research towards the practical application of this technology, we applied to be part of the "Development Project of Technology for Next Generation Thermal Power Generation / Development of Technologies for CO₂ Reduction and Utilization / Development of CO₂ utilization technology for carbonates, concrete products and concrete structures" project, publicly offered by New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO), and were accepted. Until now, we have carried out basic research jointly with Hiroshima University and Chugoku Koatsu Concrete Industries Co., Ltd. We plan to spend approximately the next three years advancing development and pilot scale tests through NEDO project to establish this technology and aim for earlier practical application. The three parties involved will contribute to preventing global warming through carbon recycling technology.
(Division of roles)
The Chugoku Electric Power Co., Inc.:
- Manufacture prototypes of CO₂ absorbing sintered material in a small-scale plant
- Investigate into optimization of a manufacturing system for CO₂ absorbing sintered material
Hiroshima University:
- Investigate into optimum mixture ratio for CO₂ absorbing sintered material
Chugoku Koatsu Concrete Industries Co., Ltd.:
- Investigate into optimum mixture and manufacturing system for CO₂ absorbing sintered material
- Manufacture prototypes of CO₂ absorbing sintered material in a small-scale plant
Partner(s)
Hiroshima University, Chugoku Koatsu Concrete Industries Co., Ltd.
Supplementary information
Other Innovation Challenges
Demonstration and development of the ultimate high-efficiency coal-fired power generation (IGFC)
The Chugoku Electric Power Company, Incorporated
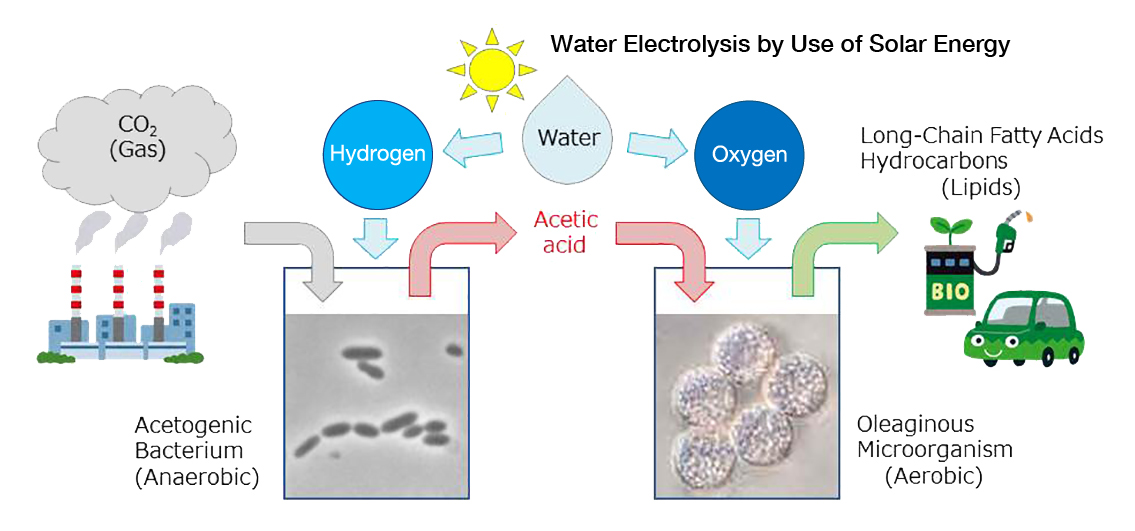
Development of a novel bioprocess to recycle CO2
The Chugoku Electric Power Company, Incorporated
Technical Development and Popularization of Efficient CO2-Use Concrete
The Chugoku Electric Power Company, Incorporated
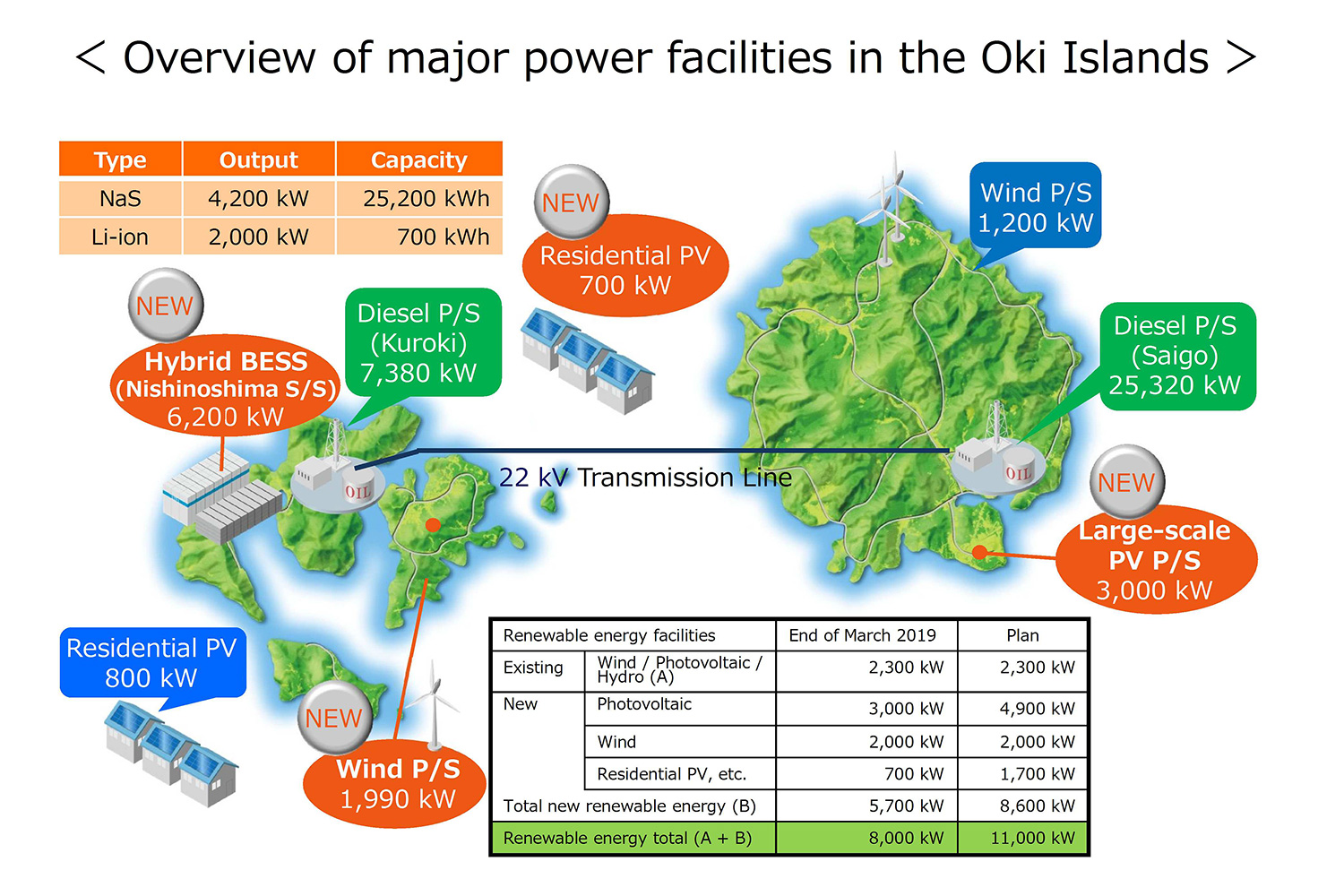
The Installation of a Hybrid Battery for Expansion of Renewable Energy Introduction in Oki Islands
The Chugoku Electric Power Company, Incorporated
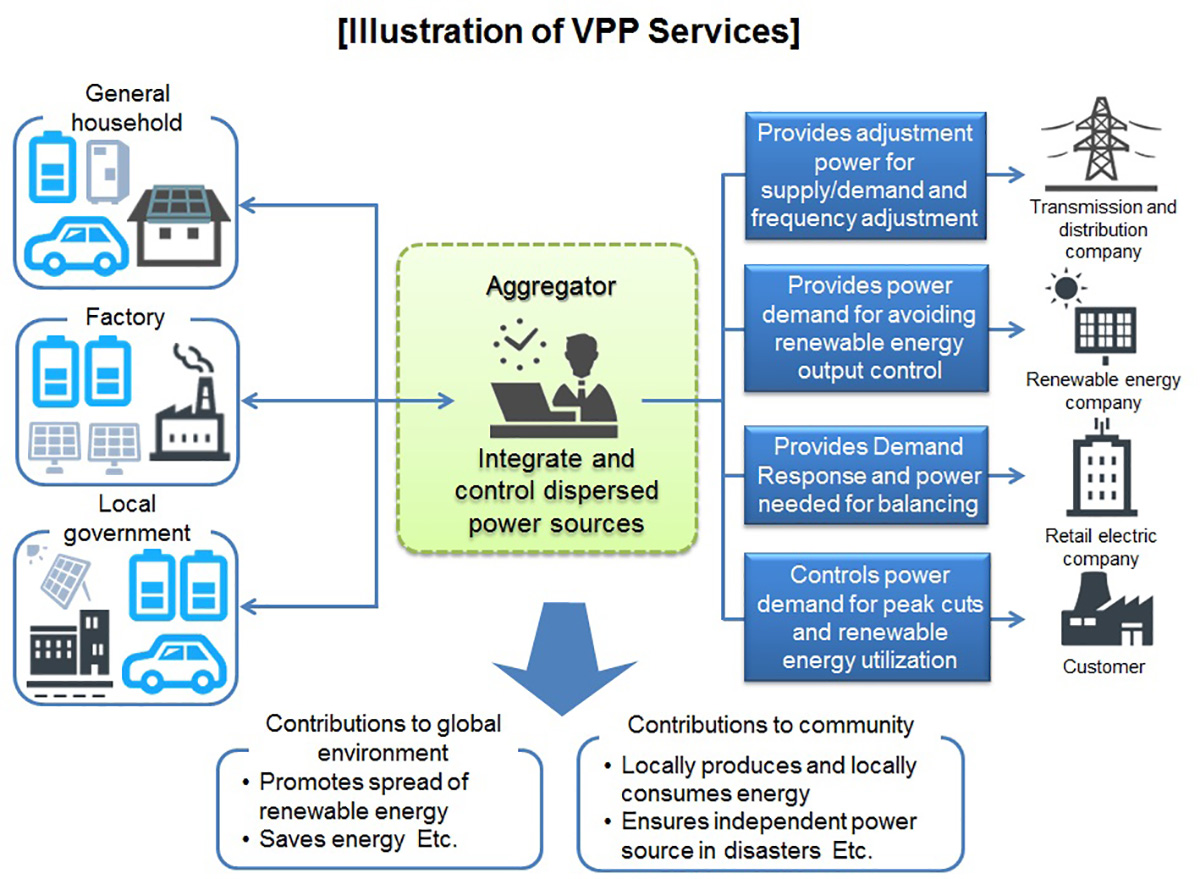
VPP Demonstration Project for Reuse Technology of EV Drive Batteries
The Chugoku Electric Power Company, Incorporated
Similar Innovation Challenges
Achieving net zero carbon emissions from paint finishing processes
Taikisha Ltd.
Activities for reducing GHG of business operations in Nissin Electric Group
Nissin Electric Co., Ltd.




-1人工光合成技術.jpg?id=2&tid=759&imageNumber=1)