Decarbonization technology of Waste to Energy Facilities
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Outline
Improvement of power generation efficiency and energy utilization of the waste incineration facilities where municipal solid wastes are treated stably and hygienically in Japan is considered as one of the key methods that can contribute to the reduction of carbon dioxide emissions.
For this reason, MHI Group will further promote energy recovery during incineration, reduce the energy consumed within the incineration facilities as much as possible, and apply the latest ICT technology to promote remote monitoring and operation of the facilities, automation, and labor saving. Our Group will also try to expand such technologies to overseas countries considering their actual situations of waste treatment.
Description
Wastes discharged from our daily lives and industrial activities are diverse, and there is a strong demand for safe and hygienic treatment of these wastes.
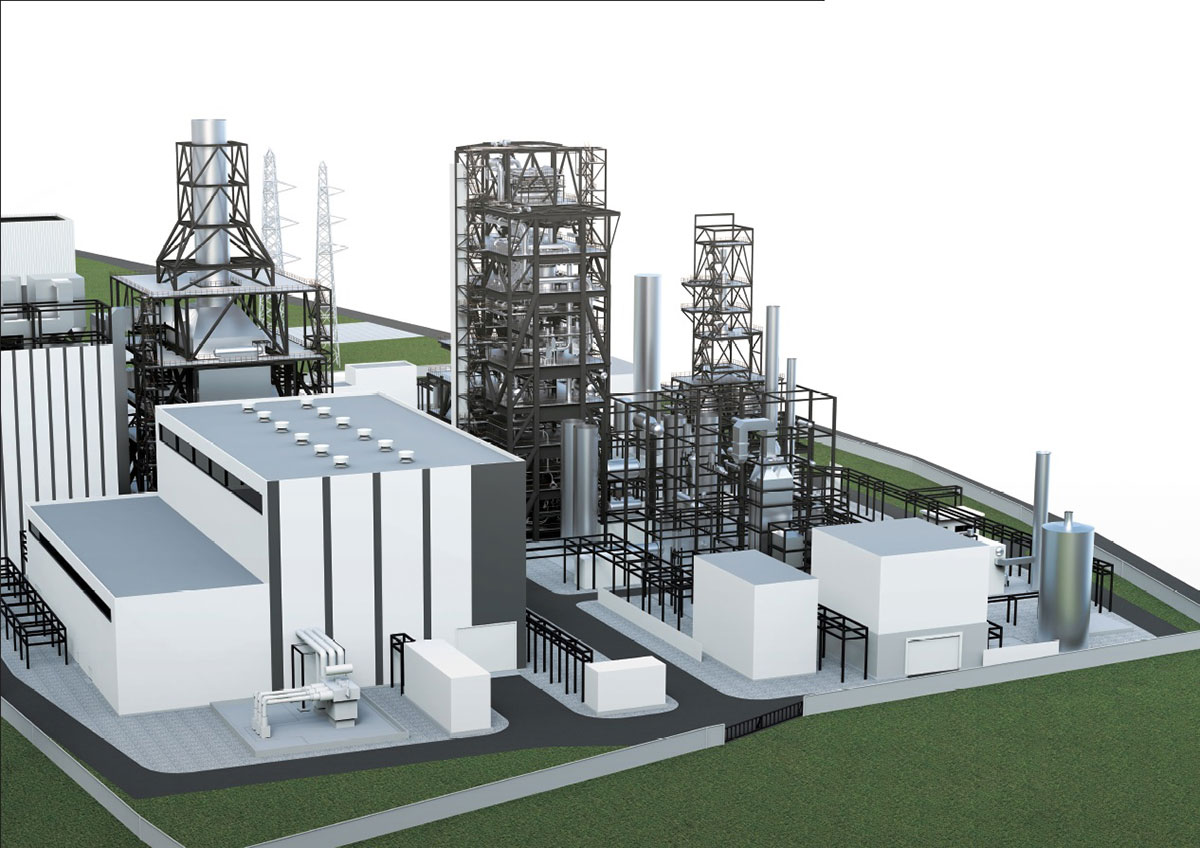
Wastes discharged daily from homes, restaurants, offices, etc. are called as municipal solid wastes. In Japan, 43 million tons of municipal solid wastes (about 920 grams per person per day) are discharged annually. About 80% of these wastes are incinerated at high temperatures and treated hygienically.
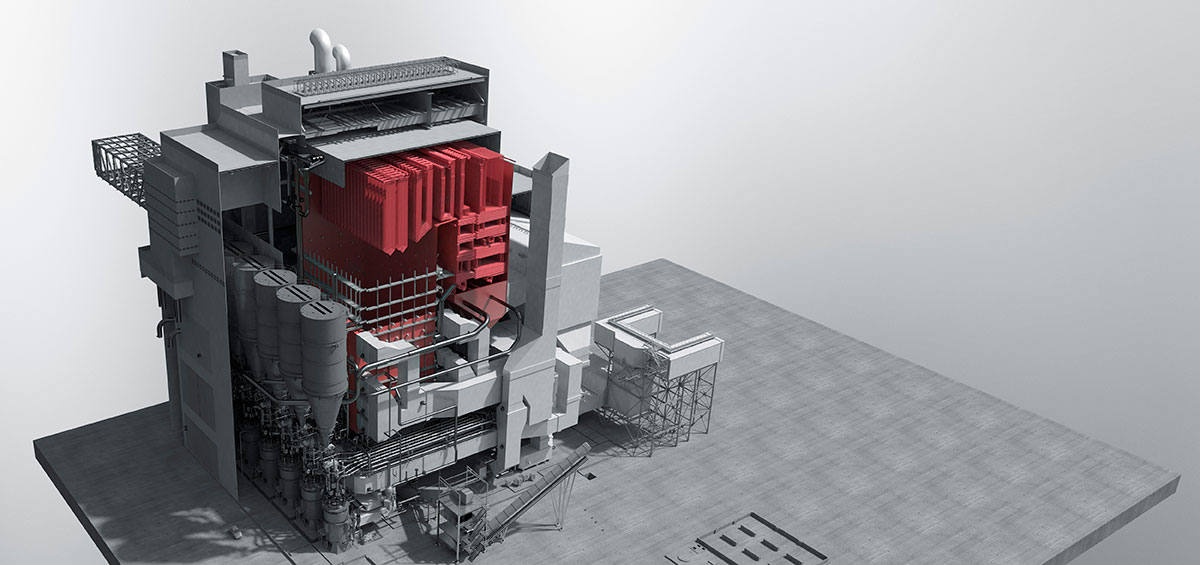
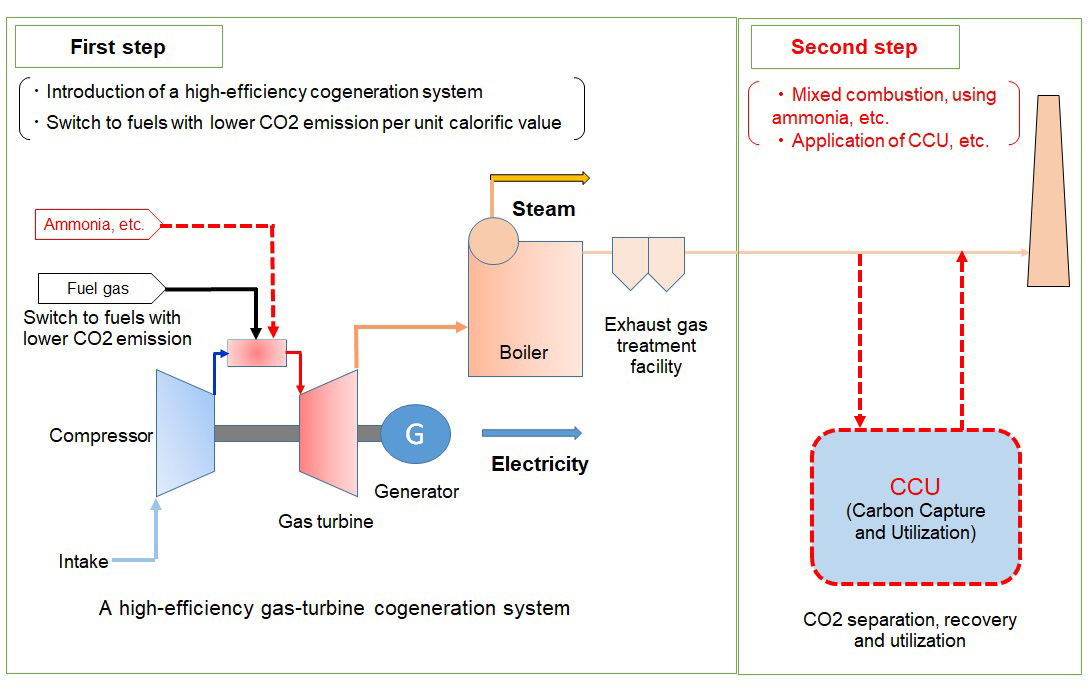
Although the amount of carbon dioxide generated from the waste sector in Japan accounts for only about 2% of the total amount generated, the high-temperature exhaust gas generated during incineration of wastes has a large amount of thermal energy. It is important to utilize this energy effectively, and at present, thermal energy is recovered by boilers, steam is generated, and electric power is generated by turbine generators.
Since boiler tubes are exposed to corrosive atmosphere due to chlorine contained in wastes, the current efficiency of power generation is limited to about 20% (the power generation efficiency of large-scale thermal power plants is more than 40% to 60%). Therefore, the boiler steam condition will be raised from the current 4MPa x 400℃ class to higher range by the technology development of boiler tube protection methods and new materials, etc, resulting in the improvement of power generation efficiency.
In addition, in order to reduce the power consumed in existing waste incineration facilities, we have been working to further promote the installation of inverters to blowers, introduction of LED lighting, introduction of solar power generation, and effective use of low-temperature waste heat.
The latest ICT technology will be incorporated into waste incineration facilities further, and efforts will be made to promote remote monitoring, remote operation, automated operation, and labor saving.
Partner(s)
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Ltd.
Supplementary information
Other Innovation Challenges
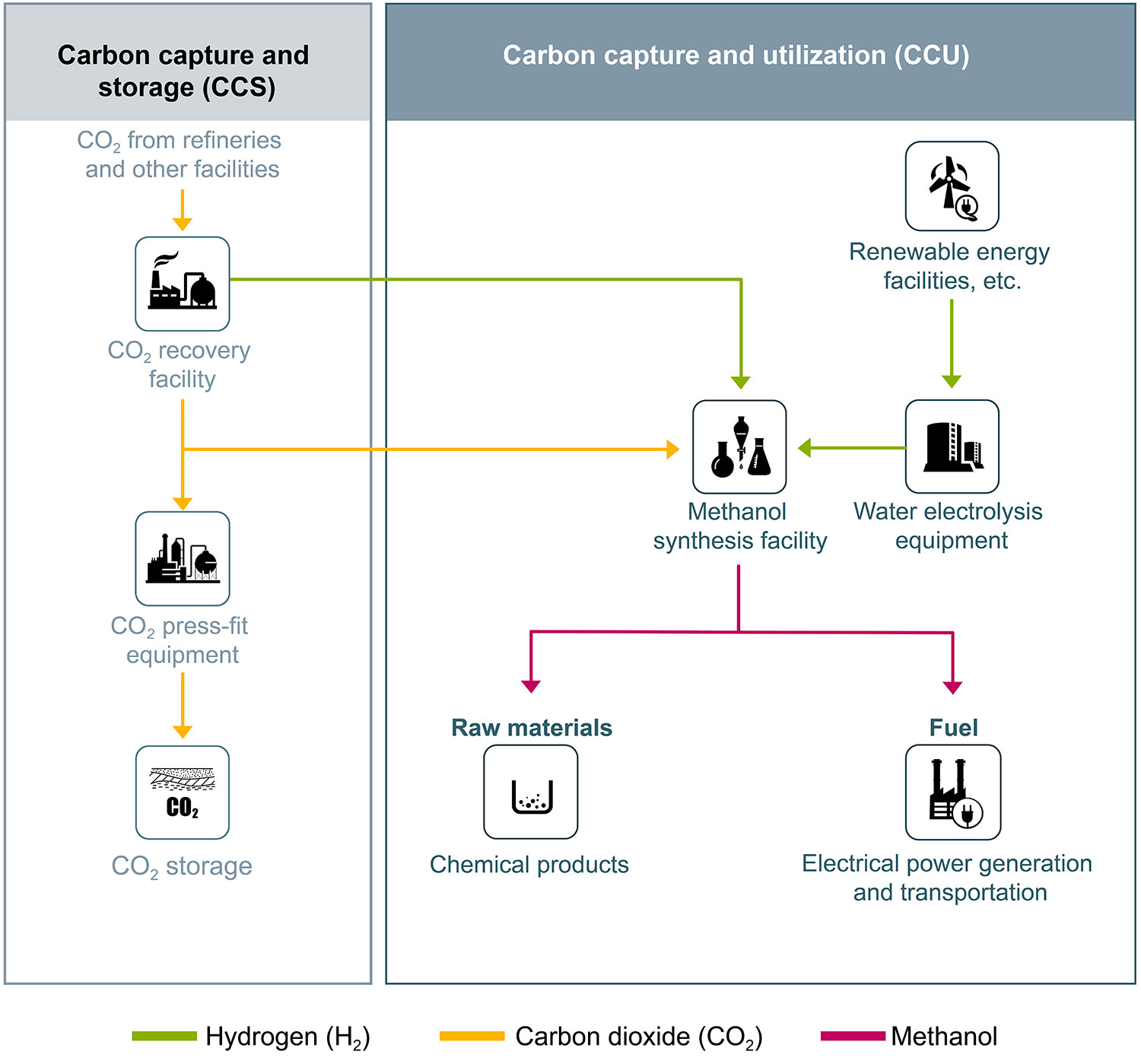
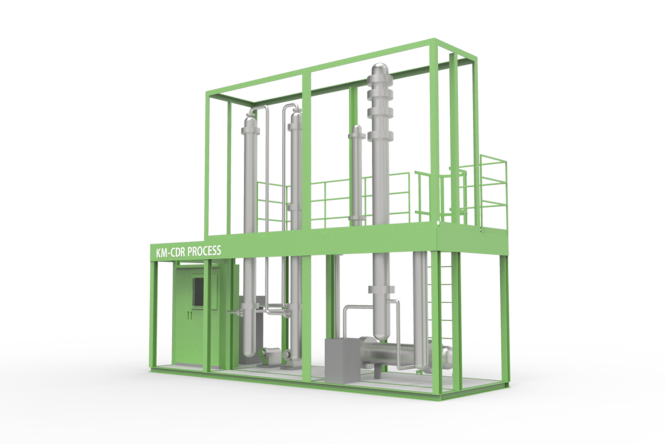
Commercialization of “carbon neutral” and “carbon negative” by implementing carbon capture technology
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Dissemination of Low-Carbon Stable Energy Infrastructure Based on IGCC Technology
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
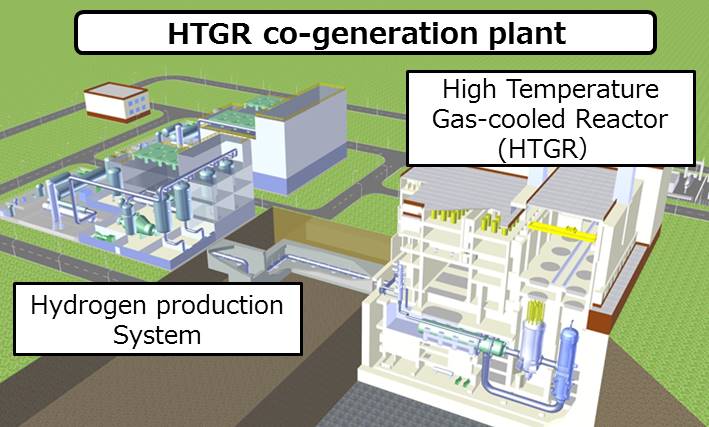
High-Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor co-generation for hydrogen production
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Promotion of centrifugal chillers using low-GWP refrigerant across full capacity range
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
QoEnTM approach – A Quantitative Index to suggest the direction toward High-quality Energy Infrastructure
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
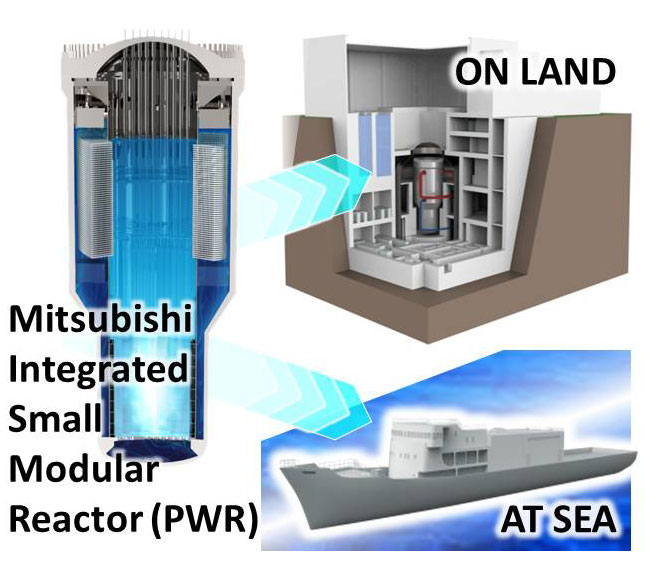
SMR Development for Small Grit Power Reactors and Mobile Reactors
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
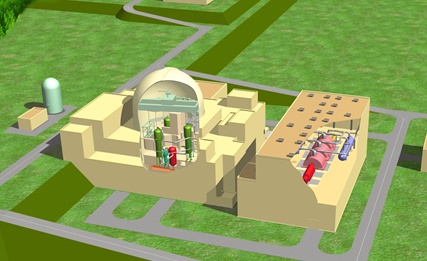
the next-generation light water reactor achieving the world's highest safety and economic efficiency
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Triple hybrid stand–alone power generation system
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
World's most efficient large GTCC power plant
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Similar Innovation Challenges
Achieve 2050 decarbonization target with Net Zero Energy House!
Sekisui House, Ltd.
Achieving net-zero emissions by promoting renewable energy use through both our monozukuri and products.
DAIWA HOUSE INDUSTRY CO., LTD.