QoEnTM approach – A Quantitative Index to suggest the direction toward High-quality Energy Infrastructure
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Outline
In line with accelerating international initiatives for climate change such as the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and the realization of sustainable development, we are working on the development of an index called QoEnTM as a quantitative index of how high-quality energy infrastructure should be defined. Our goal is to propose to urban development planners and investors, from the project planning stage, the suitable energy infrastructure that can meet the area’s energy needs and support its sustainable development. We aim to achieve this goal by quantitatively assessing the impact of the project on the area in terms of social, economic and environmental aspects.
Description
At the planning of a project such as urban development, the topics that are mainly considered include (1)what kind of society should be created, (2)in what way investment can be attracted and (3)what kind of energy infrastructure should be applied. We are developing an assessment tool to quantify indices in terms on the three aspects of society, economy and environment using public data of the region concerned. With this tool, we will be able to assess how new energy infrastructure, if introduced, can contribute to the area by quantifying and showing the gap between current indices and future indices.
With this tool, we aim to suggest the direction toward high-quality energy infrastructure to planners and investors. The term QoEnTM will be used to collectively refer to this kind of tool, and we are proceeding with its trademark registration. We intend to make this tool publicly available in the future, allowing for its use by third partners with public data.
And, QoEnTM is characterized by its capability of visualizing the current status through the three quantified indices of society, economy and environment based on public data such as the statistical data of the region concerned. The development or growth goal of the area, for example, are calculated and regarded as target indices. By comparing these two types of indices, QoEnTM can reveal any discrepancies. Furthermore, the use of a triangular radar chart to plot the three quantified indices can provide immediate comprehension in terms of the balance of the three indices and a comparison with other areas.
Phase 1 :
Select indicators related to energy to estimate indices
Phase 2 :
(1) Estimate and Visualize the current status of each index
(2) Estimate and visualize the development or growth goal as future indices
(3) Design new energy infrastructure and simulate its impact on the current status
Phase 3 :
Assess the simulation results from the perspective balance of three aspects and propose the direction for new energy infrastructure based on the results
The application of QoEnTM thus enables us to evaluate the current status in the context of the development or growth goals of the area and quantify/visualize the impact of introducing new energy infrastructure in terms of how much this introduction can bring the current status closer to the future indices.
Partner(s)
The university of New South Wales (Joint development research)
Supplementary information
MHI Technical Review Vol. 57 No.1 (2020)
https://www.mhi.co.jp/technology/review/pdf/571/571030.pdf
Other Innovation Challenges
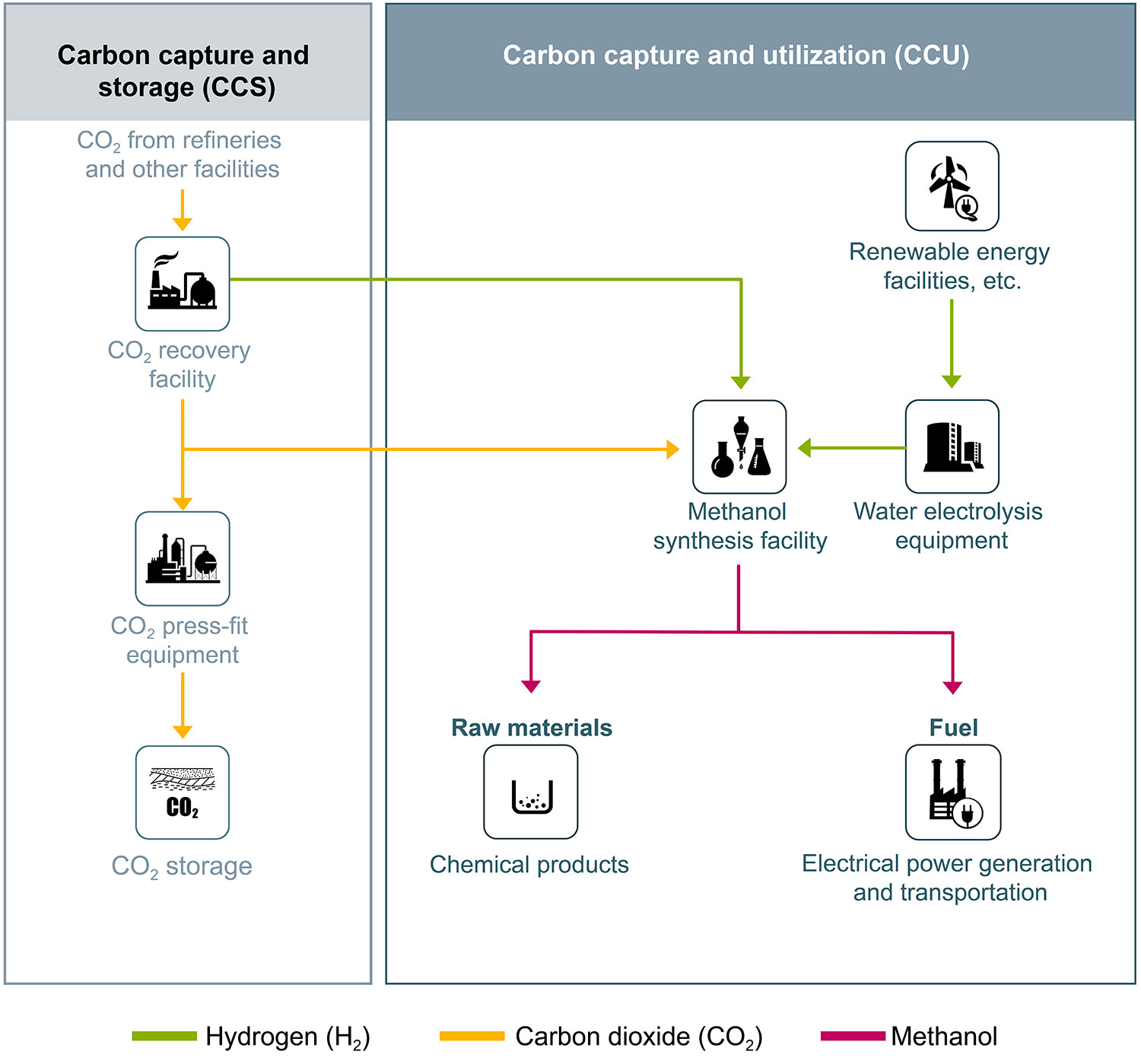
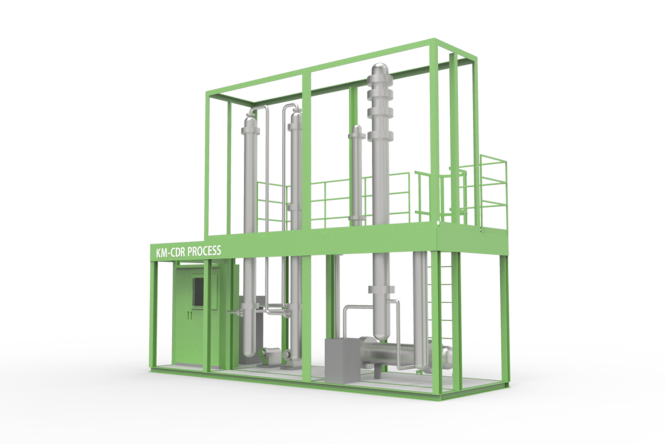
Commercialization of “carbon neutral” and “carbon negative” by implementing carbon capture technology
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
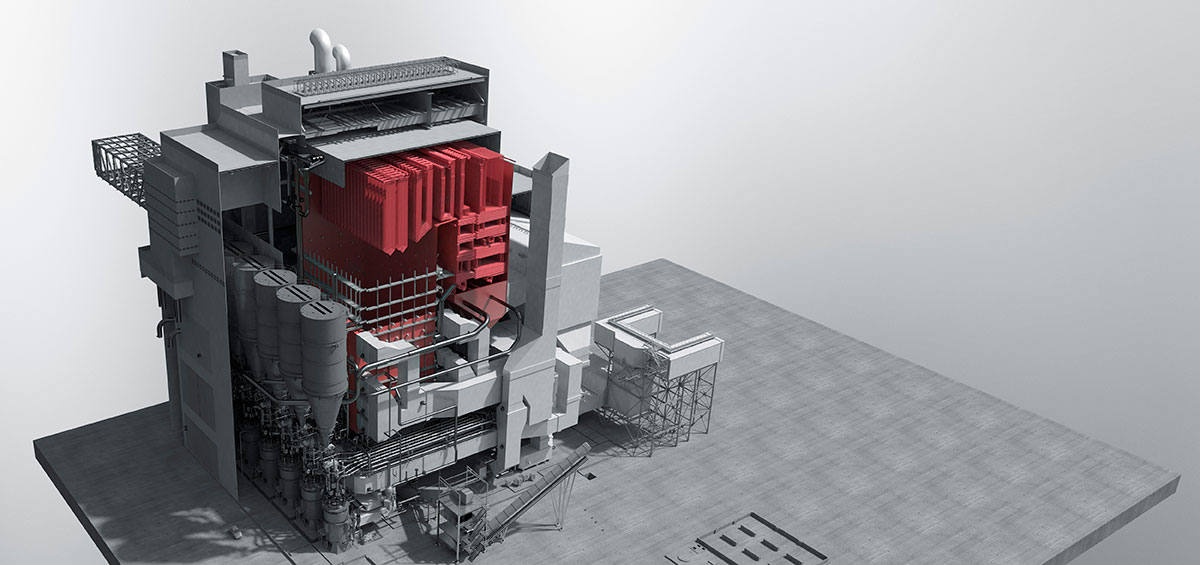
Decarbonization technology of Waste to Energy Facilities
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Dissemination of Low-Carbon Stable Energy Infrastructure Based on IGCC Technology
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
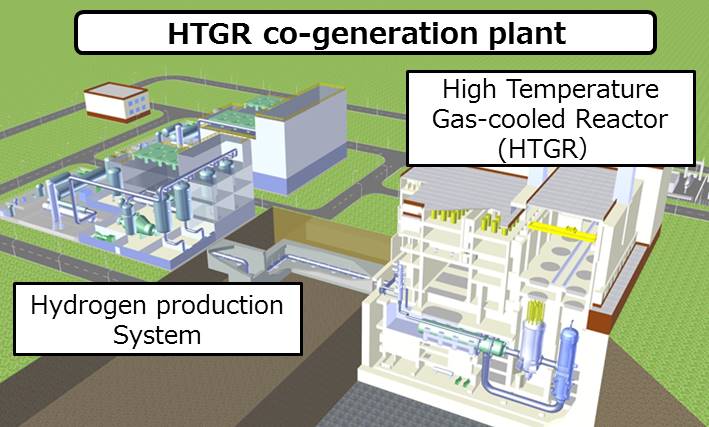
High-Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor co-generation for hydrogen production
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Promotion of centrifugal chillers using low-GWP refrigerant across full capacity range
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
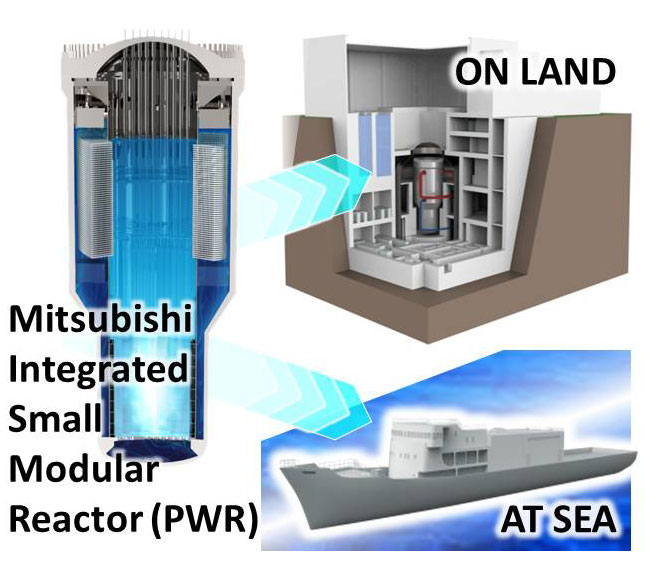
SMR Development for Small Grit Power Reactors and Mobile Reactors
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
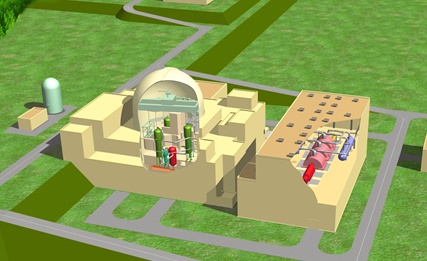
the next-generation light water reactor achieving the world's highest safety and economic efficiency
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Triple hybrid stand–alone power generation system
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
World's most efficient large GTCC power plant
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Similar Innovation Challenges
Accelarating the penetration of renewable energy resources with “Open Energy System”
Sony Group Corporation
Achieving net-zero carbon emissions from plant factories using full artificial lighting
Taikisha Ltd.
Advanced technology for buildings providing energy-saving and comfortable indoor environment (under Net Zero Energy condition)
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
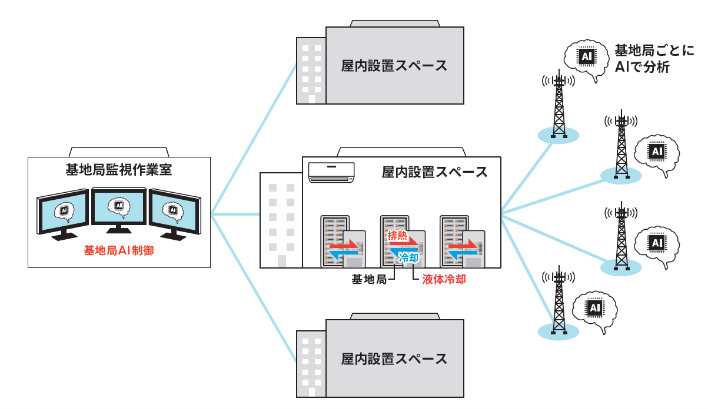
AI control reduces base station power consumption by up to 50%
KDDI CORPORATION