Development of Hydrogen Gas Turbine
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Outline
We are developing a combustor for mixed combustion and exclusive combustion of hydrogen for a large gas turbine used in a gas turbine combined cycle power plant.
The combined cycle power plant using the latest large gas turbine technology aims to achieve 64% thermal efficiency and realize the highest efficiency among all combustion engines. In the coming hydrogen society, the use of this power generation system is essential in order to efficiently utilize carbon-free hydrogen. In addition, the use of hydrogen for power generation generates a large demand for hydrogen, which contributes to the construction of hydrogen supply chains.
Description
(Status of combustor development)
MHI Group has been developing combustors for fuels containing hydrogen since the 1970s, and have delivered more than 30 units. In recent years, we have been working on the development of high-temperature, low-N0x combustors for large high-efficiency gas turbines, using the projects commissioned and subsidized by NEDO. The development of a combustor for mixed combustion of natural gas and hydrogen (H2, 30% vol) has already been completed, and it will be installed as standard equipment in our gas turbines to be shipped in the future. At the present time, the combustor for exclusive use of hydrogen is under development based on the multi-cluster combustor for IGCC used in Osaki CoolGen Project, and the development is scheduled to be completed in 2024.
(Actual project example)
In the Netherlands, a hydrogen conversion project for a gas turbine combined cycle system provided by MHI Group is underway with the aim of commencing operations in 2025. MHI Group is also cooperating with the project.
(Ammonia)
The use of ammonia as a transport medium for hydrogen has been studied, and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Engineering, Ltd. and Mitsubishi Power, Ltd are jointly developing a new combined cycle power generation plant in which ammonia is decomposed into hydrogen by using the waste heat of a gas turbine and then used as fuel for the gas turbine.
(Significance of using hydrogen in large gas turbines)
1. High efficiency. (Thermal efficiency > 64%)
2. Large quantities consumption. (Hydrogen consumption of more than 2 million FCVs at 1 gas turbine combined cycle power plant)
3. Use of cheap hydrogen. (It can use hydrogen in various manufacturing methods as impurity tolerance is high.)
4. Low Initial Cost (The natural gas-fired gas turbine can be converted to the hydrogen gas turbine with minimal modifications, enabling low and decarbonization of natural gas-fired power plant.)
Partner(s)
Mitsubishi Power, Ltd.
Supplementary information
Hydrogen Power Generation Handbook
https://www.mhps.com/catalogue/pdf/mhps_hydrogen_en.pdf
Other Innovation Challenges
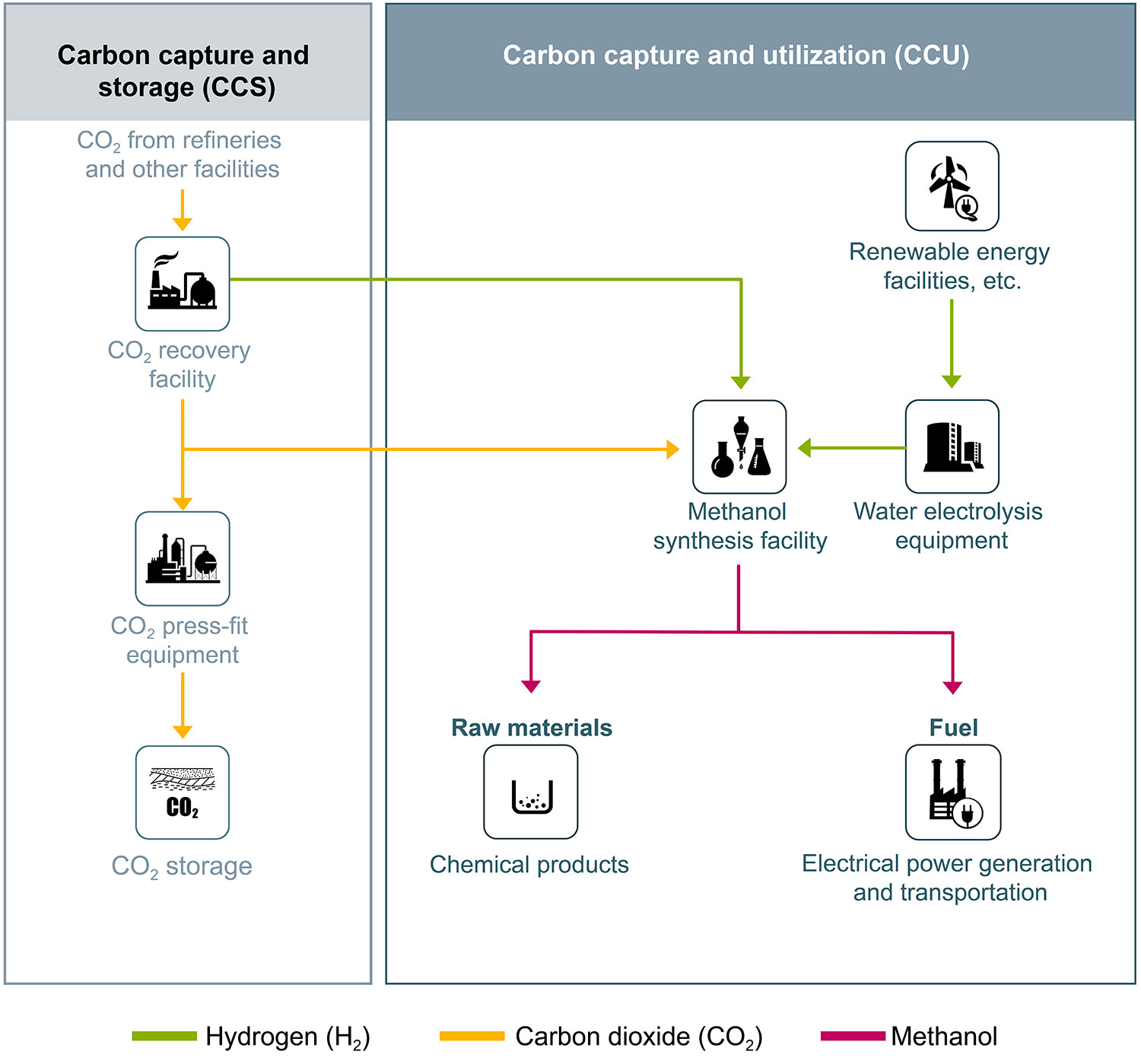
Commercialization of “carbon neutral” and “carbon negative” by implementing carbon capture technology
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Decarbonization technology of Waste to Energy Facilities
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Dissemination of Low-Carbon Stable Energy Infrastructure Based on IGCC Technology
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
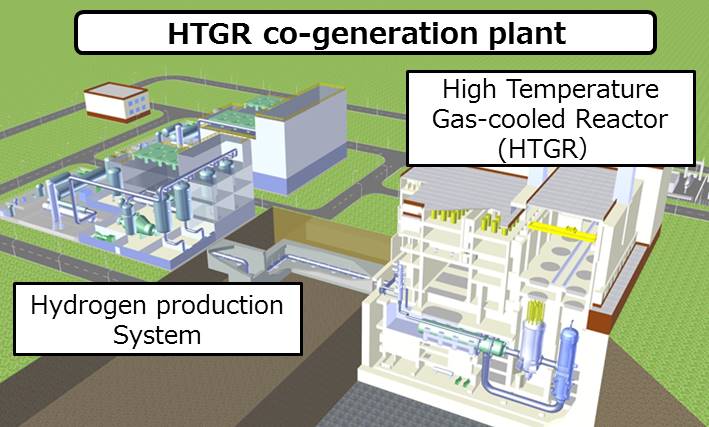
High-Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor co-generation for hydrogen production
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Promotion of centrifugal chillers using low-GWP refrigerant across full capacity range
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
QoEnTM approach – A Quantitative Index to suggest the direction toward High-quality Energy Infrastructure
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
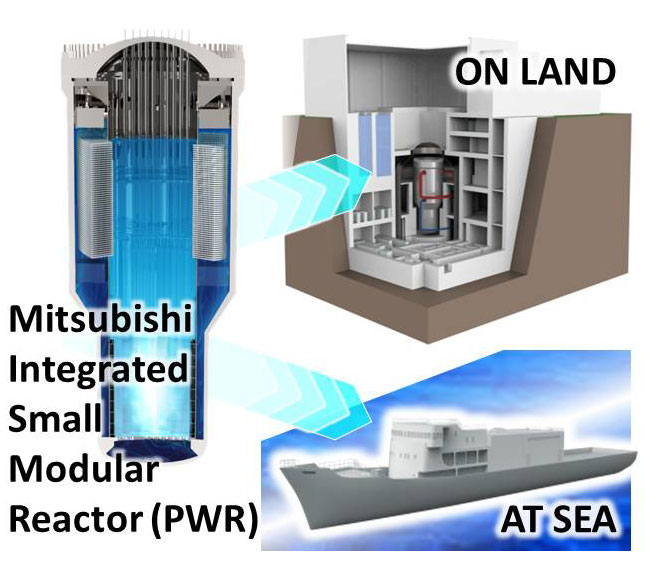
SMR Development for Small Grit Power Reactors and Mobile Reactors
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
the next-generation light water reactor achieving the world's highest safety and economic efficiency
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Triple hybrid stand–alone power generation system
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
World's most efficient large GTCC power plant
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Similar Innovation Challenges
Accelarating the penetration of renewable energy resources with “Open Energy System”
Sony Group Corporation
Achieving net-zero carbon emissions from plant factories using full artificial lighting
Taikisha Ltd.
Advanced technology for buildings providing energy-saving and comfortable indoor environment (under Net Zero Energy condition)
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
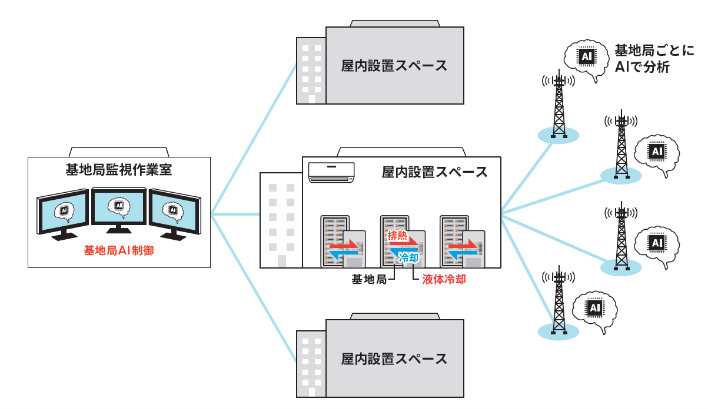
AI control reduces base station power consumption by up to 50%
KDDI CORPORATION