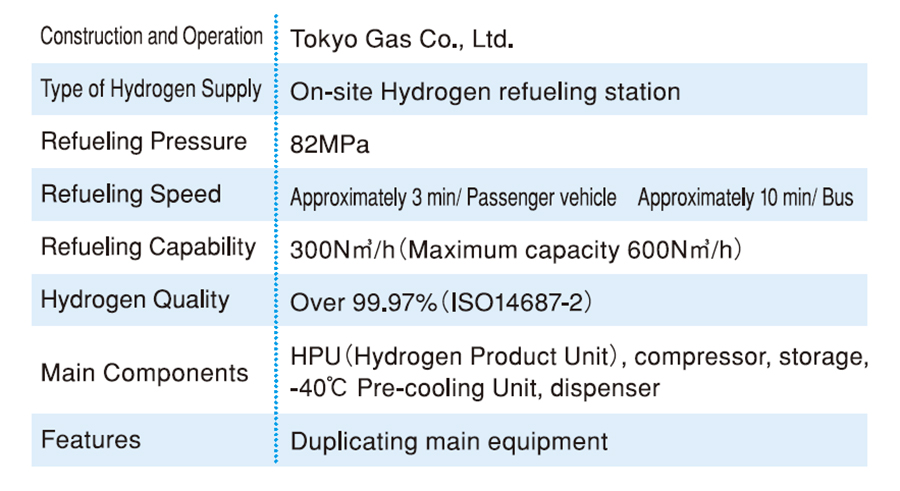
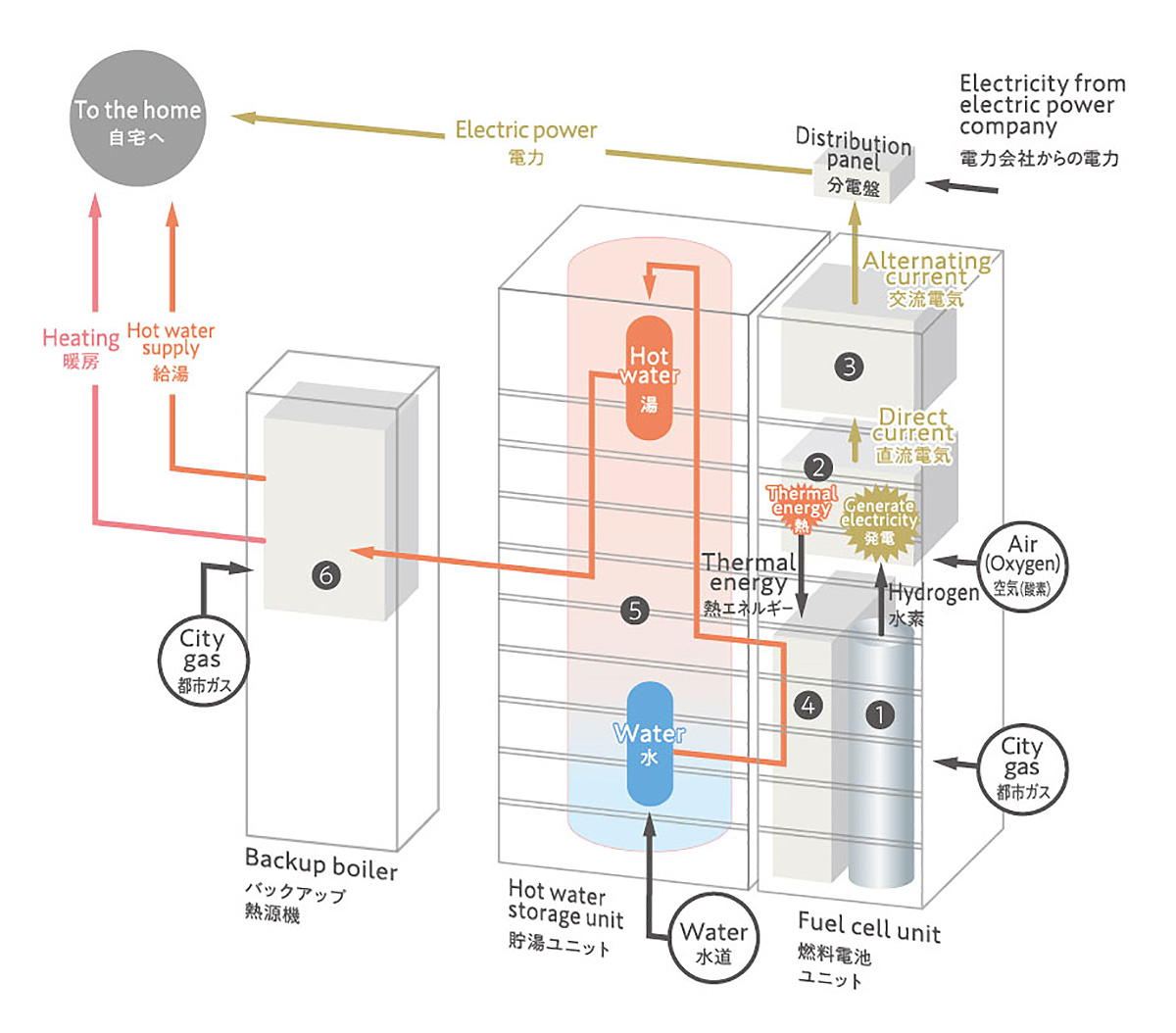
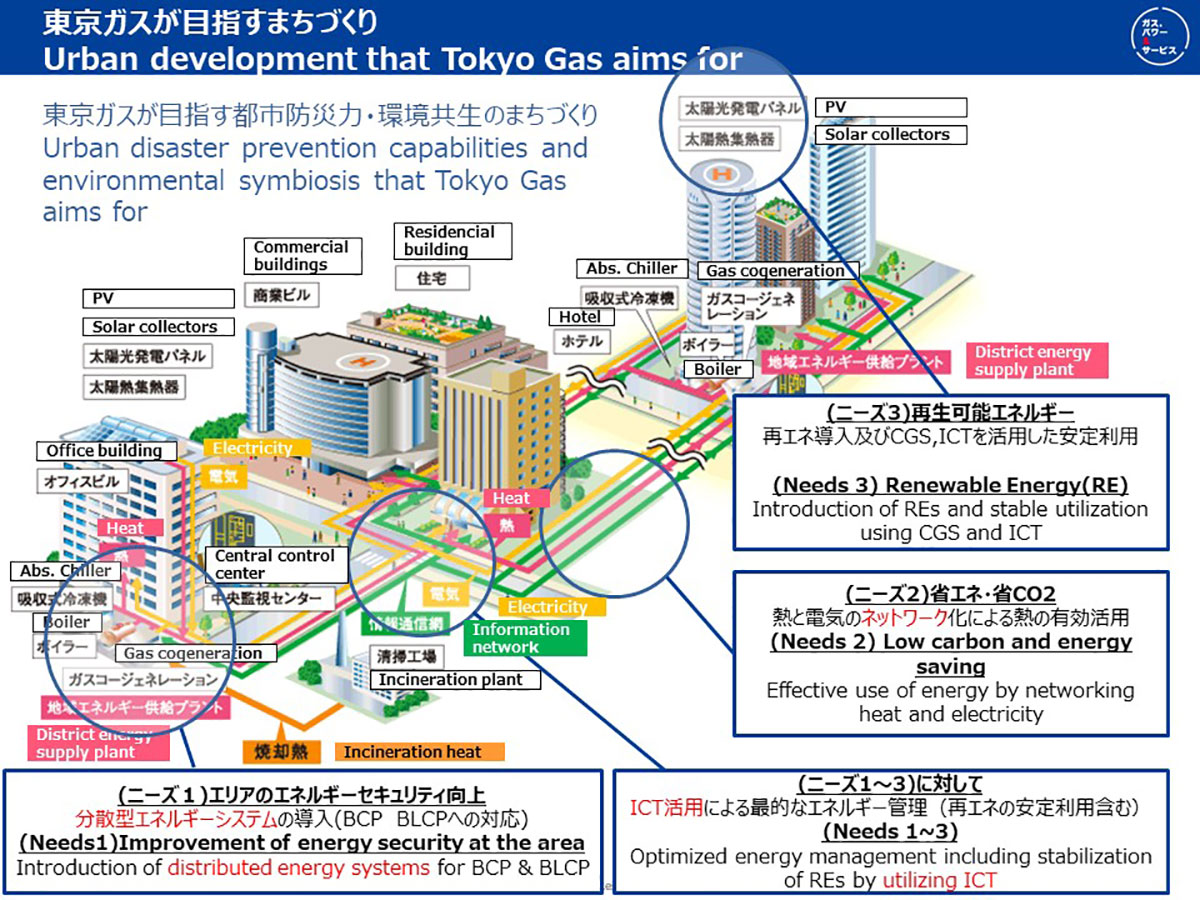
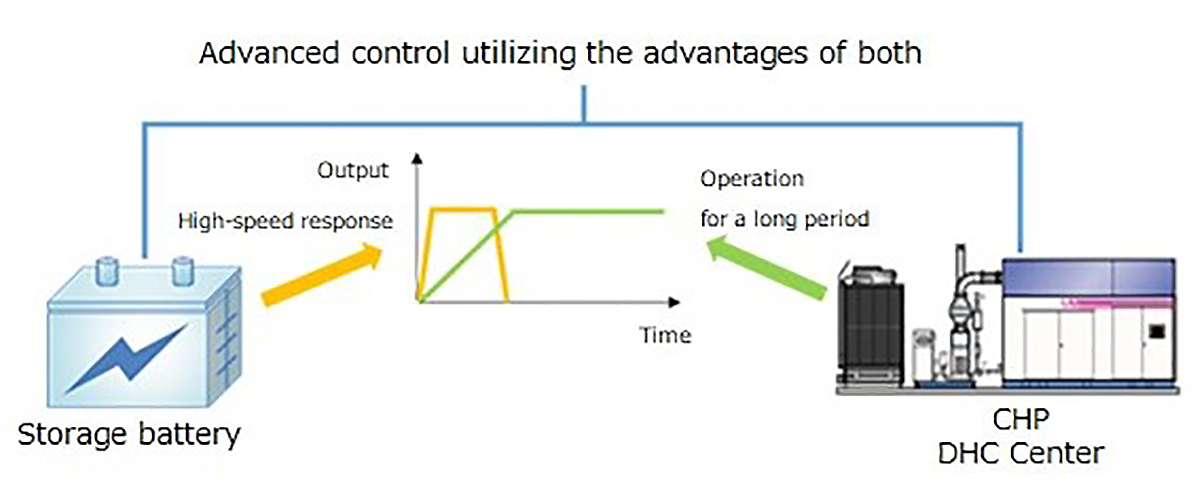
CO2 capture, use and storage (CCUS)
Tokyo Gas Co., Ltd.
Outline
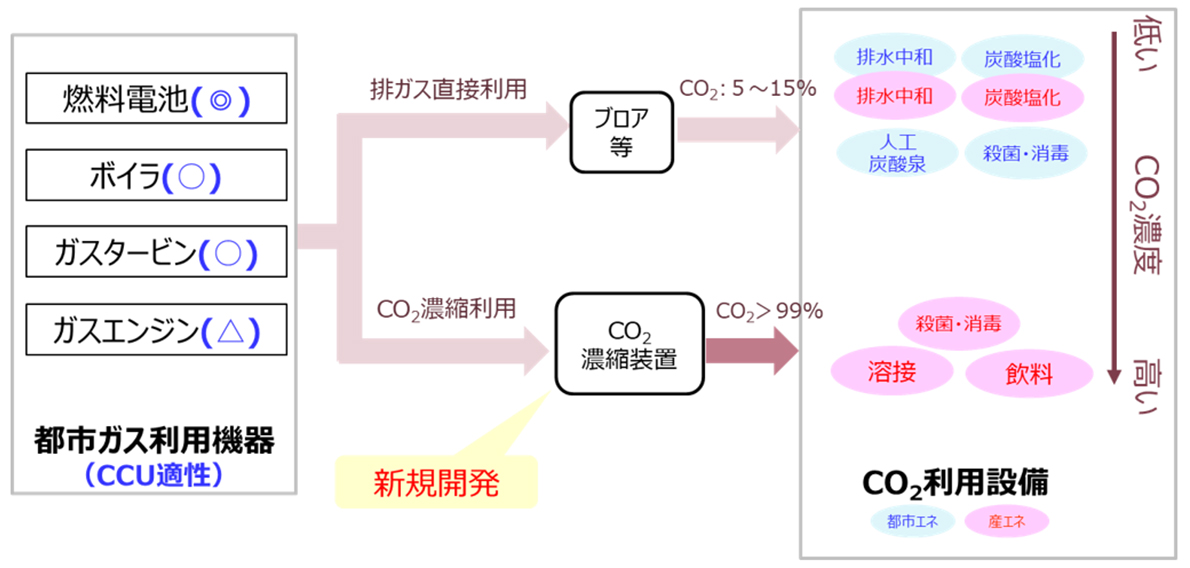
Our group will use natural gas effectively and reduce CO2 emissions through the introduction of fuel cells, CGS, etc., and by increasing the usage of energy in areas such as in smart energy networks. In addition, we plan to carry out various initiatives such as the development of energy sources that do not emit CO2, the capture, effective use and storage of CO2, and carbon offsets from forest conservation project and others. Regarding the capture, effective use and storage of CO2, we are working on the practical use of CCU technologies that capture and effectively utilize CO2 generated from gas consuming equipment and the micro-bubble technology that enables efficient CCS.
Description
Natural gas is the most environmentally friendly fossil fuel and plays a role in complementing the intermittent nature and variability of renewable energy, so its importance is likely to remain the same in the future. Our group will use natural gas effectively and reduce CO2 emissions through the introduction of fuel cells, CGS, etc., and by increasing the usage of energy in areas such as in smart energy networks. In addition, we plan to carry out various initiatives such as the development of energy sources that do not emit CO2, the capture, effective use and storage of CO2, and carbon offsets from forest conservation project and others. Of these, with regard to the capture, effective use, and storage of CO2, we are currently focusing on two technologies and working on their practical realization.
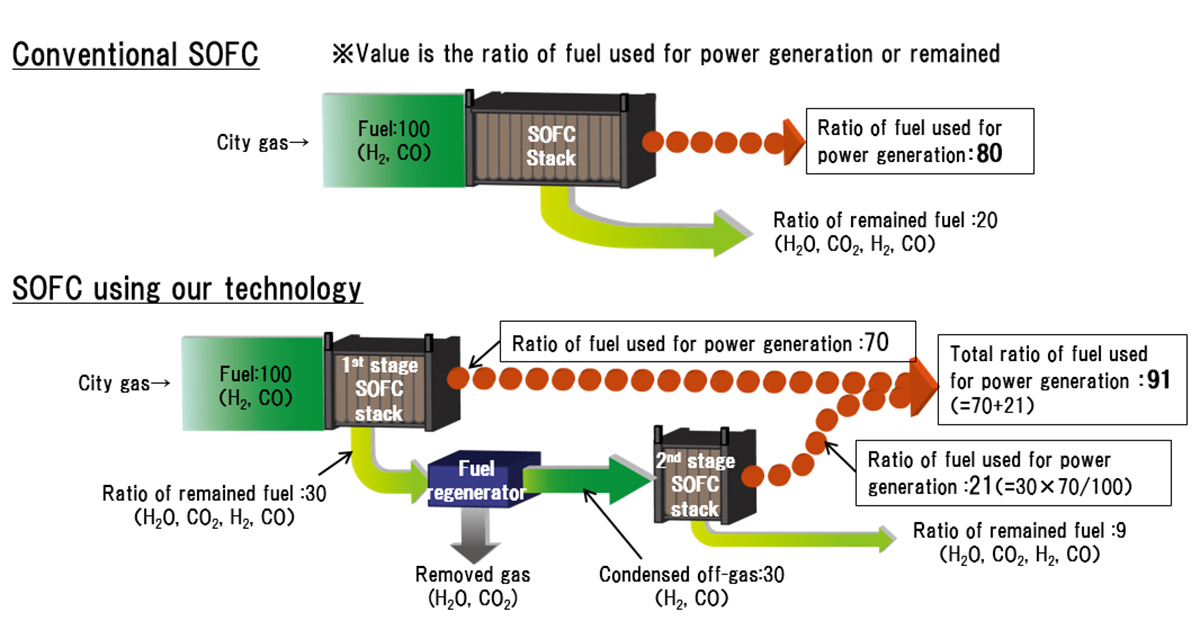
The first is the CCU technology for capturing and effectively utilizing CO2 generated from gas consuming equipment such as fuel cells, gas engines, gas turbines, and boilers at customers to whom city gas is delivered. The Group intends to promote efforts for early commercialization of this technology while expanding cooperation with other companies, research institutions, universities, and the like.
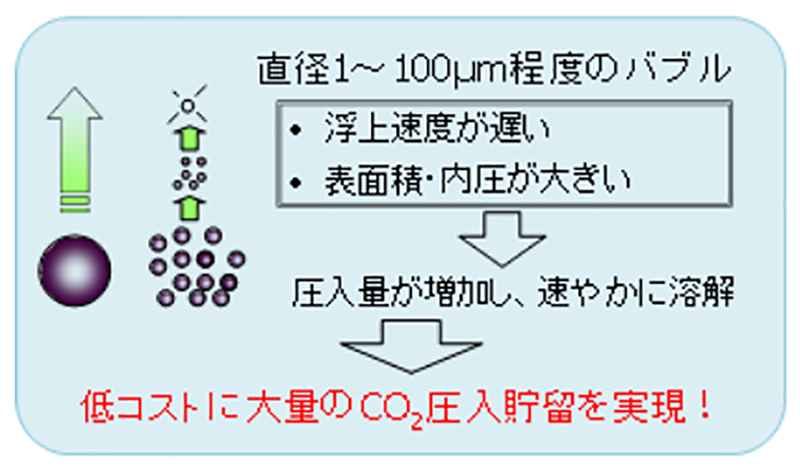
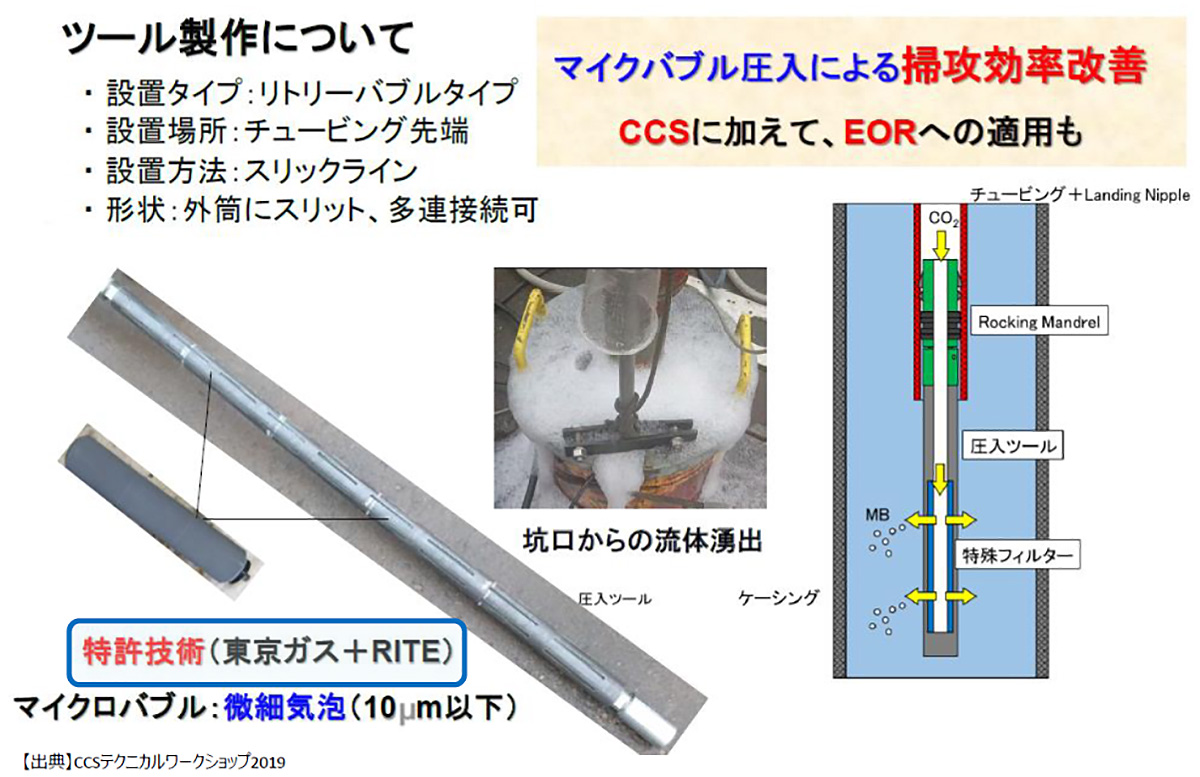
The second is the micro-bubble technology that enables efficient CCS. This technology shrinks CO2 bubbles into several tens of micrometers in diameter by a special filter and stores them. This technology enables efficient storage of large quantities of CO2 and being expected to reduce the cost of CCS. On top of that, this technology is expected to be applied to the enhanced recovery of crude oil and the like. The Group jointly holds a patent on CO2 microbubble technology for CCS with the Research Institute of Innovative Technology for the Environment (RITE) and plans to work with RITE in its commercialization.
Partner(s)
Tokyo Gas and RITE jointly hold a patent on microbubbles “storage device and storage method for stored substances (registered patent No. 5399436)”
Other Innovation Challenges
Utilization of distributed energy resources (The Virtual Power Plant)
Tokyo Gas Co., Ltd.
Similar Innovation Challenges
Accelarating the penetration of renewable energy resources with “Open Energy System”
Sony Group Corporation
Achieving net-zero carbon emissions from plant factories using full artificial lighting
Taikisha Ltd.
Advanced technology for buildings providing energy-saving and comfortable indoor environment (under Net Zero Energy condition)
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
AI control reduces base station power consumption by up to 50%
KDDI CORPORATION