Research of C2 compounds generating technology by the electrolytic reduction of CO₂
Furukawa Electric Co., Ltd.
Outline
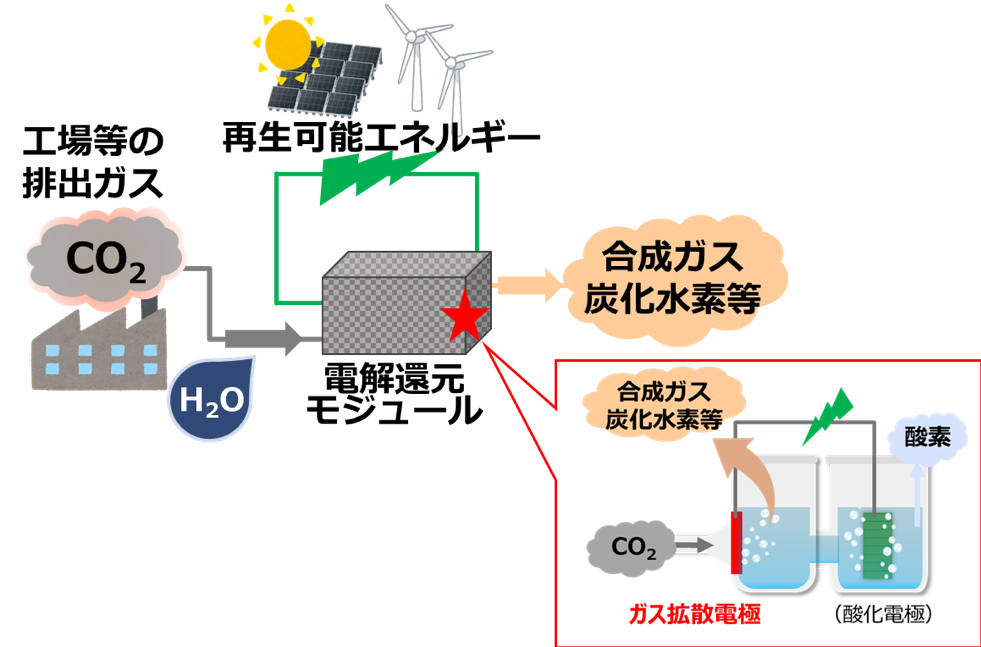
In response to COP21 agreement, innovative development in unconventional idea and new system construction are demanded for the goal of drastic reduction of CO₂ and the resolution of mid-long-term issues in energy and environment field. As a methodology of CO₂ reduction, it has been expected to convert CO₂ to useful basic chemical compounds by electrolytic reduction using renewable energy. In previous reports for the case of using CO₂ and H2O as raw materials, Copper is known as the unique cathode material which can generate C1-C3 compounds. However, the reaction mechanism is still unclear.
Description
Goal
We aim to develop a system which directly generates basic chemical compounds (C2 compounds including Ethylene) from CO₂ and H2O by electric power including renewable energy.
- To develop the catalyst added type electrode with over 80% of selectivity of C2H4.
- To develop a system of effective use of CO₂ including the catalyst added type electrode.
- Implementation after 2030.
It is known that the electrode by polycrystal copper can stably generate methane. For generating the C2 compounds which has higher additional value with high reaction selectivity, it is important to develop the catalyst added type electrode. In this research, we are developing a copper based electrode material which can generate C2 compounds with high efficiency by taking advantage of the copper material technology and the surface treatment technology in our company.
Effectiveness of CO2 reduction
In the conventional method, about 11 tons of CO₂ is emitted for the generation of one ton of ethylene. The reduction about 3 tons of CO₂ can be expected by the combination of the developing system and the electricity derived from thermal power. Furthermore, the fixation about 3 tons of CO₂ can be expected by using renewable energy in developing system.
Partner(s)
NEDO Feasibility Study Program / Feasibility Study Program on Energy and New Environmental Technology
Institute of Physical and Chemical Research
CHIYODA Corporation
The Moonshot Research and Development Program
The University of Tokyo
Osaka University
Institute of Physical and Chemical Research
Ube Industries, Ltd
SHIMIZU CORPORATION
CHIYODA Corporation
Other Innovation Challenges
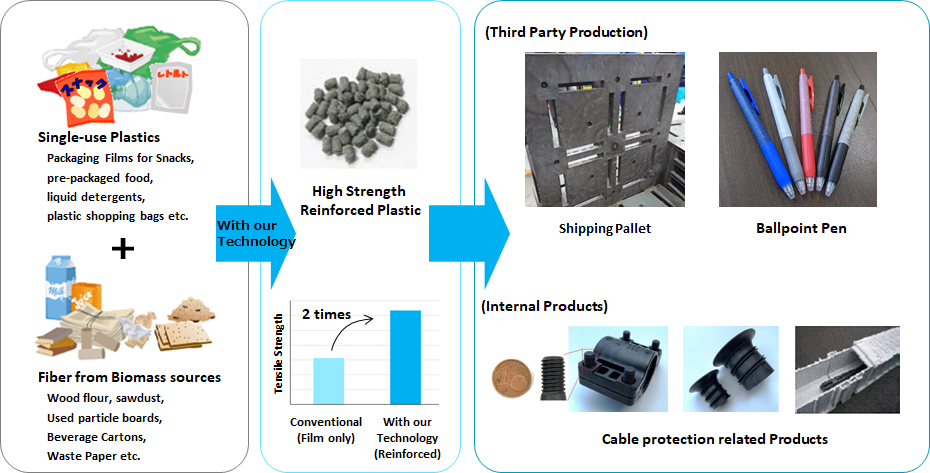
“Single-use plastics” can be mechanically recycled with a new fiber reinforcing technology for CO₂ emission reduction
Furukawa Electric Co., Ltd.
Similar Innovation Challenges
Achieving net zero carbon emissions from paint finishing processes
Taikisha Ltd.
Activities for reducing GHG of business operations in Nissin Electric Group
Nissin Electric Co., Ltd.

.png?id=2&tid=707&imageNumber=1)

-1人工光合成技術.jpg?id=2&tid=759&imageNumber=1)