Development of Cellulose nanofiber and its application
Rengo Co., Ltd.
Outline
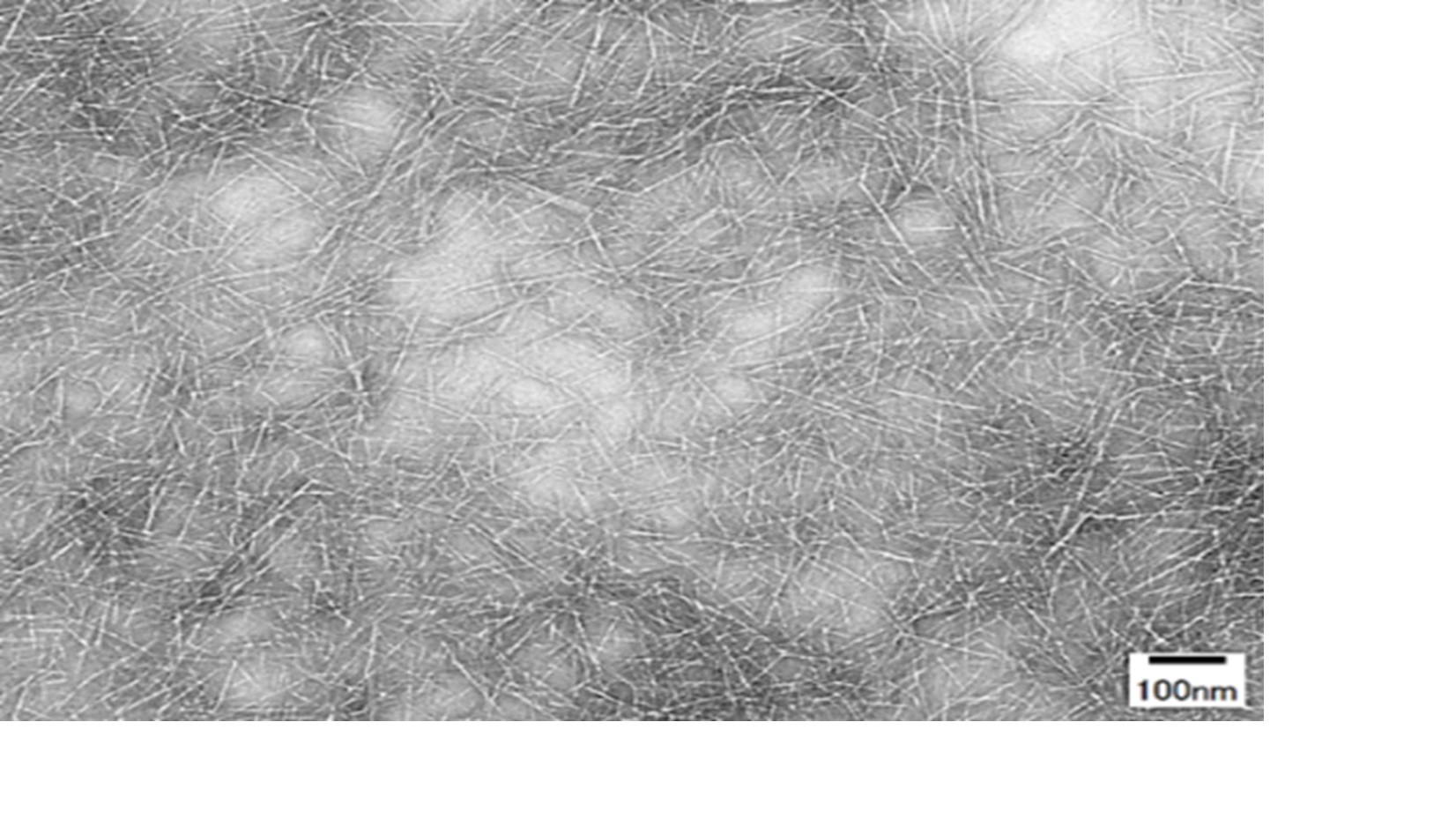
Cellulose nanofiber (CNF) is a fibrous substance made by microfiberizing fiber in wood pulp to the nanometer level (1 nm = 0.000001 mm) using chemical or mechanical processes. Due to its light weight, high strength, and specific viscosity properties, it has potential for reducing the weight of resin used in automobiles, household electric appliances and other items, and application in a variety of fields including battery materials, base materials for cosmetics, and paint materials.
Based on its cellophane production technology, Rengo has developed fine (3-10 nm diameter) and highly heat resistant CNF, and is proceeding to develop applications. Through CNF, a material mainly derived from wood, which fixes CO₂ from the atmosphere and is a renewable resource, Rengo will develop products that use less resin and have a variety of functions, and thus contribute to the realization of a decarbonized society.
Description
The Rengo Group defines itself as a “General Packaging Company” and its key word in product manufacturing and environmental management is “Less is more.” The company is developing products that generate more value with less use of resources.
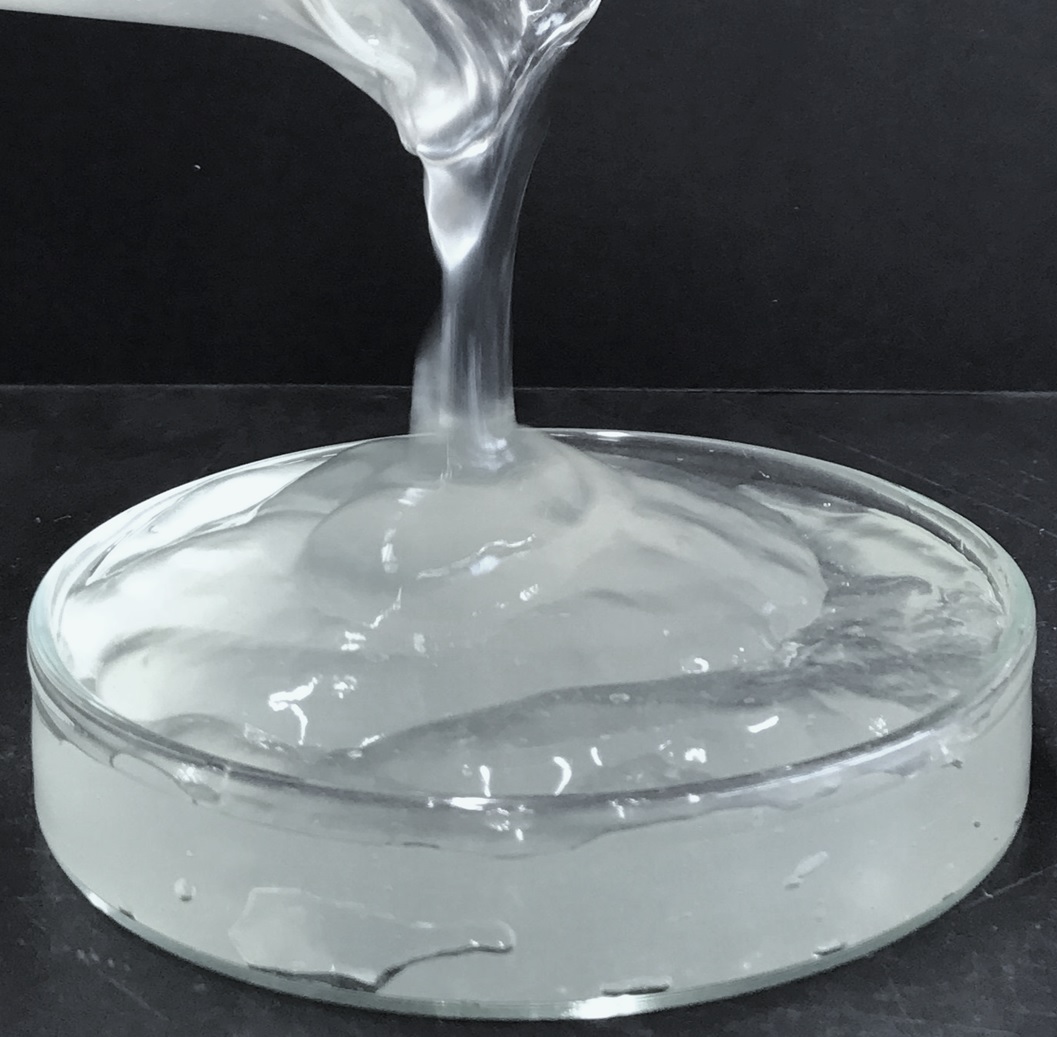
CNF is obtained by fibrillating pulp, the sustainable plant-based material, to nanometer-sized diameters. It possesses interesting properties such as high strength, high elastic modulus, low thermal expansion, and thixotropy of the suspension. These properties enable the use of CNF in various applications, and it is attracting great attention as a next-generation material. In particular, by combining a small amount of CNF with raw materials, a fine network is formed, which increases strength and has potential for reduction of life-cycle CO₂ emissions through reducing the weight of resin, rubber and similar materials.
Rengo has developed its cellophane business at the Takefu Plant (Echizen-shi, Fukui Prefecture), including cellophane film and Viscopearl beads which are made from wood pulp as their raw material, and are biodegradable in soil and in the ocean. By fibrillating cellulose xanthate, an intermediate product in the cellophane manufacturing process, xanthated cellulose nanofiber (XCNF) can be efficiently generated. XCNF can then be converted to pure cellulose nanofiber (RCNF) by removing the xanthate groups from the XCNF with simple processing. The advantages of the RCNF obtained from XCNF are that, as a non-chemically modified CNF, the fibers are extremely fine (diameter 3-10 nm) and have high transparency. Moreover, since it is cellulose, its heat resistance is close to that of pulp, its raw material, and it has the potential for use in applications such as resin molding, where high temperature processing is assumed. Its strengthening effect in some resins, rubber and similar materials has been recognized, and Rengo will actively collaborate with companies and universities on fundamental research and product development with the aim of early commercialization, and in this way contribute to the creation of a low carbon society.
Further development points
1. Introduction of a pilot plant and establishment of mass production technology
2. Development of applications
Supplementary information
Cellulose-related products
https://www.rengo.co.jp/english/products/functional/index.html
Rengo to Develop New Cellulose Nanofiber Through Application of Cellophane Production Technology
https://www.rengo.co.jp/english/news/2018/18_e_news_008.html
Other Innovation Challenges
CO₂ reduction during the lifecycle by providing corrugated packaging products
Rengo Co., Ltd.
Similar Innovation Challenges
Achieving net zero carbon emissions from paint finishing processes
Taikisha Ltd.
Activities for reducing GHG of business operations in Nissin Electric Group
Nissin Electric Co., Ltd.




-1人工光合成技術.jpg?id=2&tid=759&imageNumber=1)