Balancing greenhouse gas emissions and absorption by using bioplastics
Mitsubishi Chemical Holdings Corporation
Outline
The Mitsubishi Chemical Holdings Group is making efforts in various fields to transform from one-way consumption of materials and energy to a recycling-oriented society that focuses on the carbon cycle. The bioplastics introduced here are solutions that have been developed and commercialized with the power of comprehensive chemistry, utilizing our expertise in biotechnology-chemical-polymer-processing that we have cultivated over many years. Although plastics have helped enrich people's lives for the seventy to eighty years, the consumption and waste of fossil resources has become a global problem.
To respond to this challenge, our bioplastics:
・ use plant-derived raw materials to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and obtain functions that
cannot be obtained from fossil resources.
・ contribute to the balance between greenhouse gas emissions and absorption by substituting conventional used plastic waste disposal with biodegradability
Description
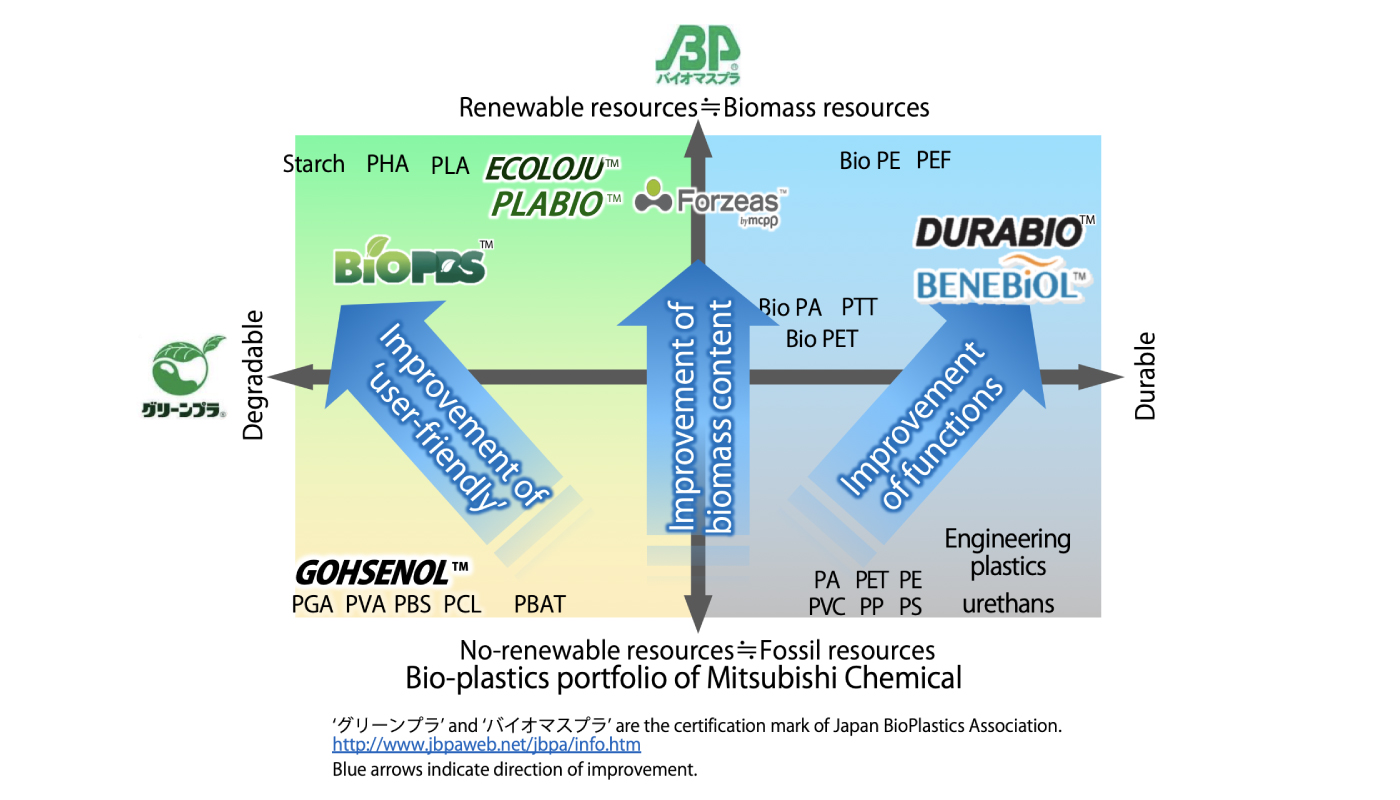
Bioplastics are classified mainly into two types of environmentally friendly materials: biomass (biobased) plastics, which are made mainly from plants, and biodegradable plastics, which degrade completely in the soil. We are promoting a lot of initiatives to create new materials, enhance functions and stably produce biomaterials so that customers and society can accept bioplastics as a solution for creating a recycling-oriented society.
i.…Utilization of biomass
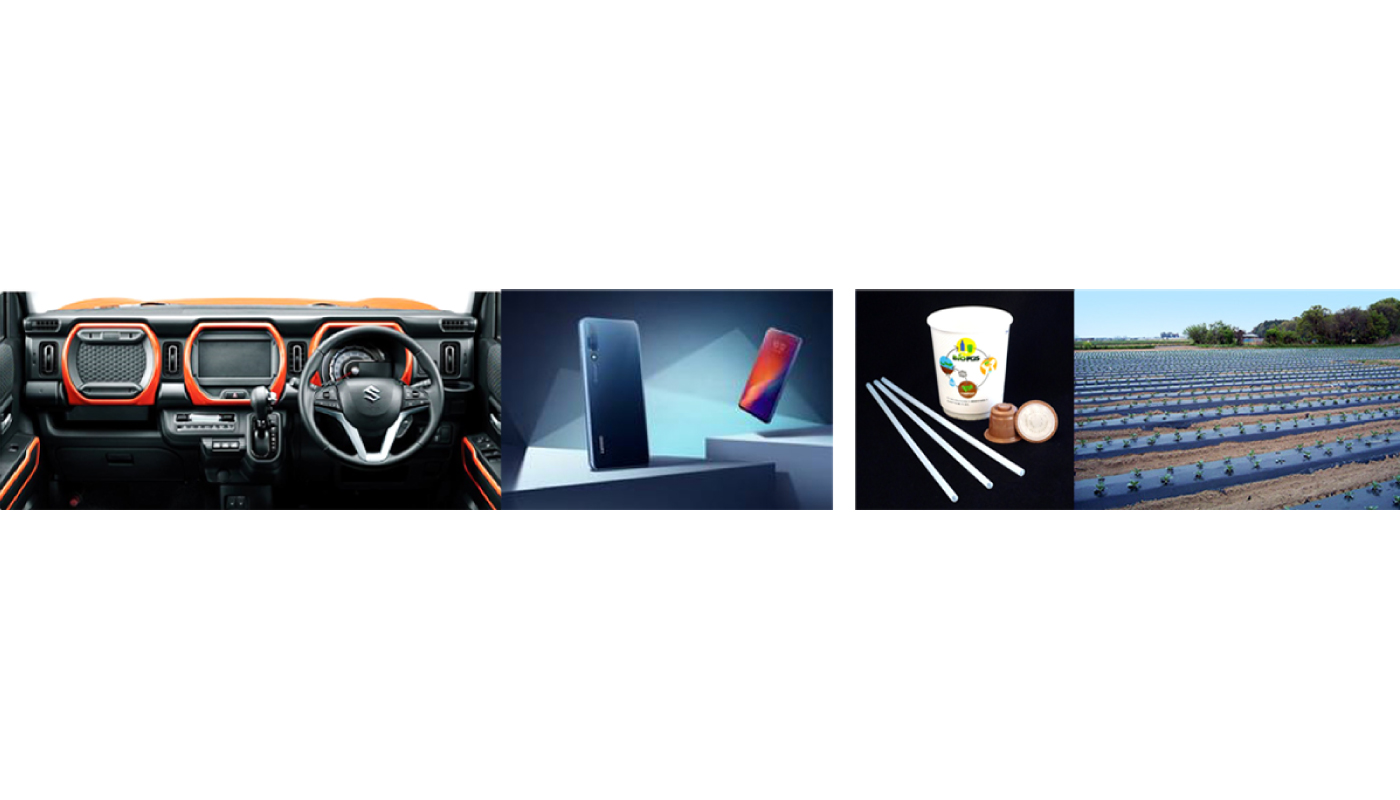
DURABIO, an engineering plastic made from plants, BENEBiOL, a polycarbonate diol used as a raw material of high-performance polyurethane resin, and ECOLOJU, a plant-based film and sheet, can reduce the consumption of fossil resources. Biomass, the raw material, minimizes greenhouse gas emissions into the atmosphere because plants produce biomass by fixing CO2 from the air.
Another advantage of using biomass is that the unique characteristics of biological molecules can be used in enhancing the performance of plastics. DURABIO uses raw material called isosorbide originated from plants, which is difficult to produce from fossil resources. Thanks to this, DURABIO has properties that cannot be easily combined with other transparent plastics, such as optical properties very similar to glass, surface hardness, strength and high durability. At present, it has begun to be used in applications such as electronic equipment, automotive interiors / exteriors and glass substitution. These days, the application of the property that bacteria hardly adhere to the surface is being promoted. Polyurethane resin made with BENEBiOL is different from common ones. It has strong resistance to various chemicals such as human sweat and acids / alkalis, and has a soft texture and durability with application for automotive interiors, sports apparel and paints. They are also highly valued since their raw materials do not compete with food supply issues.
ii. Use of biodegradation
While the property of degradation is inconsistent with the durability of plastics, by controlling when and how degradation begins, we can make the plastics perform their best during use and disappear after they have finished their role. Thus, this is a new way for plastics in society of the future. Because many chemical companies have been actively promoting compounding and multi-layering in response to request for enhanced functionality, products such as food packing materials, sanitary goods and applications, and agricultural materials have become increasingly difficult to separate or recycle. These applications that use a lot of energy for disposal and recycling can take advantage of the biodegradable properties alongside other approaches.
BioPBS is a biodegradable plastic that can be used as general plastic and decomposes into water and CO2 in soil by microorganisms in nature environment. Since BioPBS is also made from plant-derived biomass, the increase in atmospheric CO2 due to its decomposition can be minimized. BioPBS is easy to mold and easy to mix with other materials, and it easily creates layers. Its applications are expanding to include difficult-to-recycle or difficult-to-dispose consumables such as paper cups and straws, agricultural films and tapes, coffee cartridges, etc. In addition, GOHSENOL has been used increasingly as a raw material for manufacturing chemicals, packaging containers and adhesives because of its properties as a surfactant and the property of disallowing the passage of air. Since it is quite water-soluble and biodegradable, applications utilizing this feature are under development.
iii. Bioplastics Initiatives
・ Biomass
As a chemical manufacturer, we continue to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by replacing as much plastic materials as possible with plant-based material. In cooperation with research institutes and companies in Japan and overseas, we are working to obtain raw materials and materials with stable and economically acceptable costs.
Molecules created by living organisms have more potential to confer new functions on plastics. We want to take advantage of IT, such as materials informatics, which we are developing internally and externally, and to try to extend functions from molecular structures we do not know well yet.
In order to utilize the functions provided by biomass molecules to reduce energy consumption, for example, by reducing the weight of automobile parts, new combinations of materials and technologies are being realized, while adopting new processing technologies such as 3D printers. This can contribute to possible modeling design and product manufacturing process innovation. IT technologies also play an active role here.
・ Biodegradability
The biggest challenge in using biodegradable plastics is to ensure that the degradation begins and plastic disappears completely when the user wants. Since the use of plastics varies widely, it is very difficult to control the decomposition as desired in all cases, but first, we are developing a method of manufacturing plastic products and the elements that promote the decomposition of the products. We suppose one key is to elucidate the mechanism of how decomposition proceeds. In the future, we aim to incorporate a mechanism into plastic molecules that initiates decomposition in response to external stimuli. These initiatives will be pursued through industry-government-academia joint development projects.
We have not yet fully exploited the properties of biodegradability. We will consider with members of the value chain how to apply biodegradability to reduce greenhouse gas and energy consumption, that is, how products are provided and what kind of services are available. FORZEAS is a plastic solution product that combines biodegradable plastics and is tailored to provide the properties required by customers. The life cycle analysis using a biodegradable film made of FORZEAS for agriculture, which is a government commissioned project, is expected to be a model case for observing the balance of greenhouse gases from production to disposal.
Activities in industry groups related to chemicals, plastics and bioplastics and national and international initiatives
Research and commissioned business with SIP, New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization, Ministry of the Environment, etc.
Partner(s)
Activities in industry groups related to chemicals, plastics and bioplastics and national and international initiatives
Research and commissioned business with SIP, New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization, Ministry of the Environment, etc.
Supplementary information
DURABIO
https://www.m-chemical.co.jp/products/departments/mcc/sustainable/product/1200363_7166.html
BENEBiOL
https://www.m-chemical.co.jp/products/departments/mcc/c4/product/1200297_7124.html
ECOLOJU
https://www.m-chemical.co.jp/products/departments/mcc/sustainable/product/1200363_7166.html
BioPBS
https://www.m-chemical.co.jp/products/departments/mcc/sustainable/product/1200364_7166.html
GOHSENOL
https://www.gohsenol.com/doc/outl/outl_01.shtml
FORZEAS
https://www.mitsubishichem-hd.co.jp/products/detail.php?id=2312
Other Innovation Challenges
Efforts to make practical use of mobility for realizing net zero carbon emissions
Mitsubishi Chemical Holdings Corporation
Research and development of artificial photosynthesis for realizing a sustainable carbon cycle
Mitsubishi Chemical Holdings Corporation
Similar Innovation Challenges
Accelarating the penetration of renewable energy resources with “Open Energy System”
Sony Group Corporation
Achieving net-zero carbon emissions from plant factories using full artificial lighting
Taikisha Ltd.
Advanced technology for buildings providing energy-saving and comfortable indoor environment (under Net Zero Energy condition)
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
AI control reduces base station power consumption by up to 50%
KDDI CORPORATION