Realizing “Zero-Carbon Steel”
JFE Holdings, Inc.
Outline
【JFE Steel Corporation】
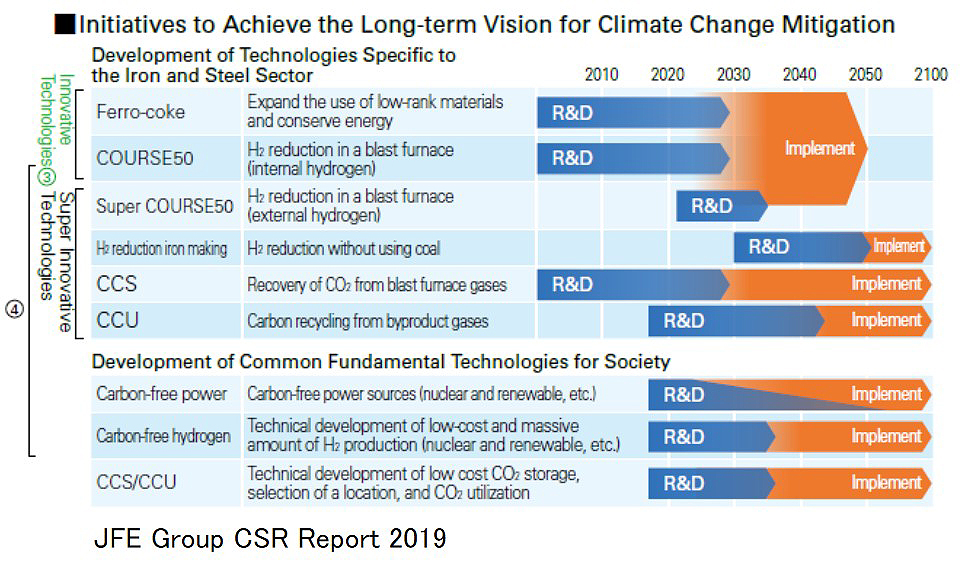
The Japanese iron and steel industry will take on the challenge of developing super innovative technologies to achieve “zero carbon steel,” which goes beyond innovative blast furnace steelmaking technologies such as COURSE50 and ferro-cokes for commercialization in 2030 and manufactures steel with zero CO2 emissions.
JFE Steel Corporation, as a main member of JISF project, will pursue the Super COURSE50, which further increases the hydrogen reduction ratio in the blast furnace, hydrogen reduction steelmaking by 100% hydrogen reduction, and CCU and CCS technology development in parallel.
Description
In November 2018, the Japan Iron and Steel Federation formulated the "Japan Iron and Steel Federation's Long-Term Vision for Climate Change Mitigation – A Challenge Towards Zero-Carbon Steel". In this initiative, hydrogen reduction steelmaking technology to achieve “zero carbon steel”, CCS (Carbon Capture and Sequestration) to separate and capture and store CO2 generated in the steelmaking process, and CCU to generate valuable materials from CO2 (Carbon Capture and Utilization).
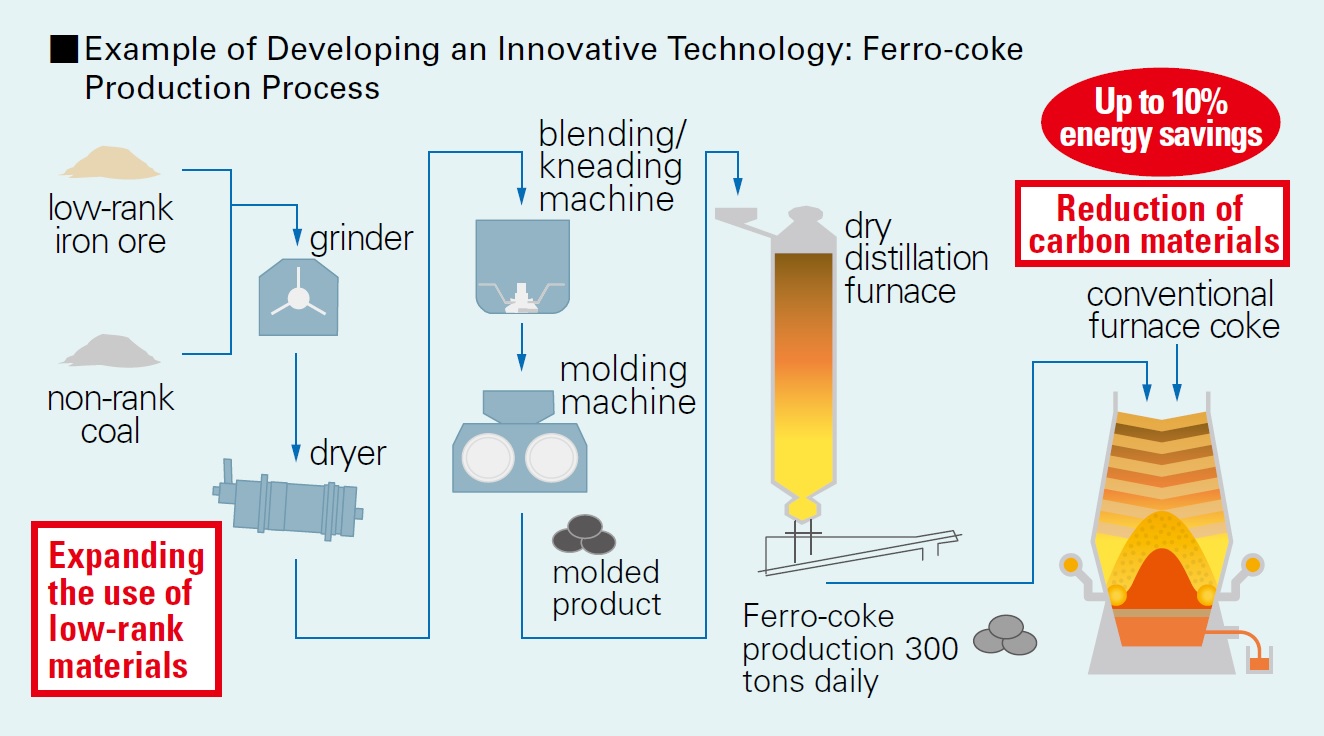
As the first step, the hydrogen reduction steelmaking is promoting the COURSE50 project, which focuses on increasing the hydrogen reduction ratio in the blast furnace by using hydrogen generated inside the steel works. As the second step, the challenge is to further increase the hydrogen reduction ratio in the blast furnace by using external hydrogen, super COURSE50. As the third step, we will work on development of hydrogen reduction non-blast furnace based process that uses only hydrogen as a complete reducing agent. We aim to develop these super-innovative technologies by 2050.
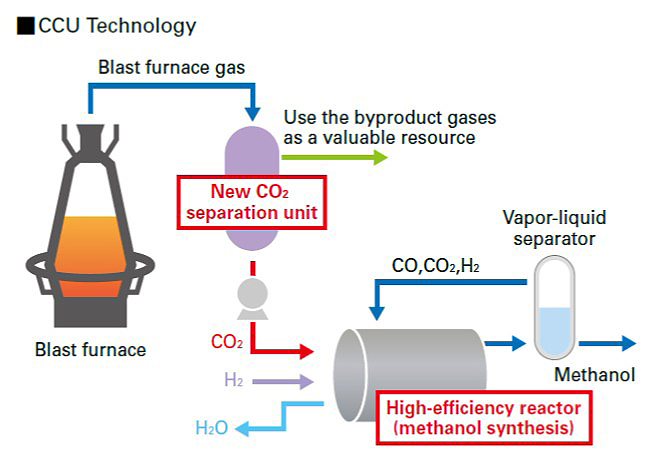
In CCS and CCU, we will challenge the development of low energy consumption CO2 separation and capture technology from blast furnace exhaust gas, and the search and development of CCU technology that can be realized in integrated blast furnace steelworks.
It should be noted the practical application of hydrogen-reduction ironmaking process is premised that hydrogen is developed and maintained as a common energy carrier for the society, be stably supplied at low cost, in addition to being carbon free. Moreover, the implementation of CCS requires, in addition to the development of cheap transportation and storage technologies for large quantities of CO2, solving issues that go beyond technical aspects, such as securing CO2 storage sites, acceptance from society, implementing entities, and distribution of the economic burdens. Thus, JFE Steel Corporation will work in cooperation with the government and other industries to realize “zero carbon steel”.
Partner(s)
METI, The Japan Iron and Steel Federation, New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization(NEDO), The Japan Research and Development Center for Metals(JRCM)、Nippon Steel Corporation, JFE Steel Corporation, and Kobe Steel, Ltd.,
Supplementary information
“Zero-Carbon Steel”
https://www.jisf.or.jp/business/ondanka/zerocarbonsteel/index.html
Other Innovation Challenges
Challenge for development of super‐innovative technologies focusing on “Carbon‐recycling Blast Furnace+CCU”
JFE Holdings, Inc.
Multi-site integrated energy network services for energy saving
JFE Holdings, Inc.
Realization of decarbonization by developing hard carbon for next-generation lithium-ion battery "All-polymer battery"
JFE Holdings, Inc.
Technology of improving water quality of sea area by use of steel slag products
JFE Holdings, Inc.
Similar Innovation Challenges
Accelarating the penetration of renewable energy resources with “Open Energy System”
Sony Group Corporation
Achieving net-zero carbon emissions from plant factories using full artificial lighting
Taikisha Ltd.
Advanced technology for buildings providing energy-saving and comfortable indoor environment (under Net Zero Energy condition)
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
AI control reduces base station power consumption by up to 50%
KDDI CORPORATION

.png?id=2&tid=812&imageNumber=1)