Maintaining grid stability for the mass introduction of renewable energy
The Federation of Electric Power Companies of Japan
Outline
In the Strategic Energy Plan, toward 2050, efforts for the utilization of renewable energy as the major power source was described. In the main power grid system, as the renewable energy ratio increases, the number of connected synchronous generators, such as thermal power, decreases, and the system inertia and short-circuit capacity decrease, making it difficult to operate and control the power grid system. On the other hand, even in a load system including power distribution, if a large number of distributed power sources, storage batteries, EVs, and the like are connected, uncertainty in the system increases, and voltage / current control becomes complicated.
The Federation of Electric Power Companies of Japan and partners have developed basic grid analysis tools for nationwide coordination of transmission operators and grid stability in the event of a grid accident, so that the stability of the power grid can be maintained even in the future when these events are expected. We will develop a system simulator to evaluate them and a dynamic behavior calculation method for the distribution system using an instantaneous value analysis program, etc., and make efforts to contribute to the mass introduction of renewable energy.
Description
[Development of power system analysis tool for nationwide coordination of transmission operators]
There is a concern that the introduction of large amounts of intermittent renewable resources will reduce the predictability of power flow in operational planning, and increase uncertainty. For this reason, models and tools related to PV and wind power generation developed by the Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry (CRIEPI) will be improved, which are essential for power system analysis at the time of mass introduction of renewable energy. The power system analysis utilizing developed models and tools enables the system operators to smoothly carry out their system planning and operations both in each area and in the wide area.
[Maintaining power system stability at the time of disturbance under the mass introduction of renewable energy]
With the mass introduction of renewable energy into the electric power system, power system stability may be deteriorated due to various phenomena especially in the event of a disturbance. In order to solve this problem, the full analog power system simulator developed by CRIEPI, which has been utilized to develop various power system technologies for a long time, will be supplemented with physical models, which enables to simulate power system with the mass introduction of renewable energies, to improve power system analysis technology. In this way, we will develop and verify technologies to maintain power system stability in the event of a disturbance when a large amount of renewable energy is introduced.
[Development of Dynamic Simulation Methods for Distribution Systems]
Wide use of photovoltaic power generation systems causes voltage-rise and other problems in distribution systems, and this forces complicated operations of distribution systems and requires dynamic simulation methods for assessing these phenomena. Because of this, CRIEPI has been developing an electromagnetic transient (EMT) program which is capable of reproducing waveform-level behaviors of distribution systems including power-electronics converters used in renewable-energy power generation systems. Aiming at further smarter operations of distribution systems where electric vehicles (EVs) and battery-energy storage systems (BESSs) are interconnected, we will develop EMT simulation models of EVs and BESSs and enable dynamic simulations including these devices for coordination of existing and newly-introduced devices. It should be noted that this development also enables simulations of various abnormal phenomena and power-quality problems which will occur in distribution systems.
Partner(s)
Hokkaido Electric Power Co., Inc., Tohoku Electric Power Co., Inc., Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc., Chubu Electric Power Co., Inc., Hokuriku Electric Power Co., Inc., The Kansai Electric Power Co., Inc., The Chugoku Electric Power Co., Inc., Shikoku Electric Power Co., Inc., Kyushu Electric Power Co., Inc., The Okinawa Electric Power Co., Inc., Electric Power Development Co., Inc., Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry
Other Innovation Challenges
Enhancing power sector resilience against disaster risks
The Federation of Electric Power Companies of Japan
Improvement in Efficiency and Flexibility of Thermal Power
The Federation of Electric Power Companies of Japan
Promotion of electrification and energy conservation
The Federation of Electric Power Companies of Japan
Promotion of hydrogen use
The Federation of Electric Power Companies of Japan
Similar Innovation Challenges
Accelarating the penetration of renewable energy resources with “Open Energy System”
Sony Group Corporation
Achieving net-zero carbon emissions from plant factories using full artificial lighting
Taikisha Ltd.
Advanced technology for buildings providing energy-saving and comfortable indoor environment (under Net Zero Energy condition)
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
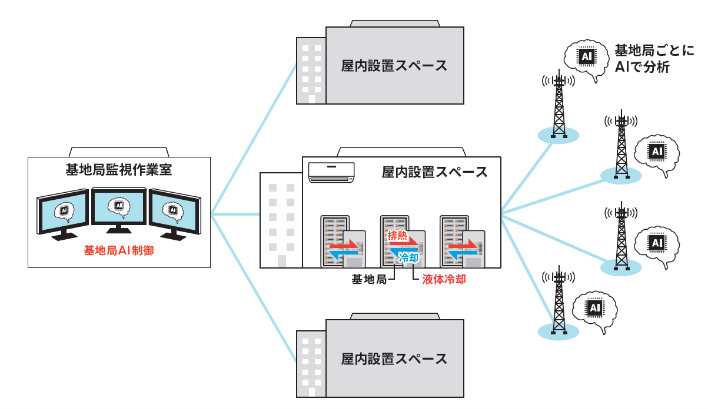
AI control reduces base station power consumption by up to 50%
KDDI CORPORATION