Increase power generation efficiency using concentrator photovoltaic System (CPV)
Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd.
Outline
Our goal in CPV is to realize more environmentally friendly power generation equipment than ordinary solar power generation equipment by shortening energy payback time and extending life by increasing power generation efficiency. With regard to redox flow batteries, the goal is to improve the performance of more environmentally friendly storage batteries for power systems and to realize cost reductions so that they can be widely disseminated and penetrated into society with the important feature that there is no risk of fire at all. Improving the balance between electricity supply and demand and increasing the amount of renewable energy that can be introduced by CPV and other will create a society that can promote the introduction of various types of renewables.
Description
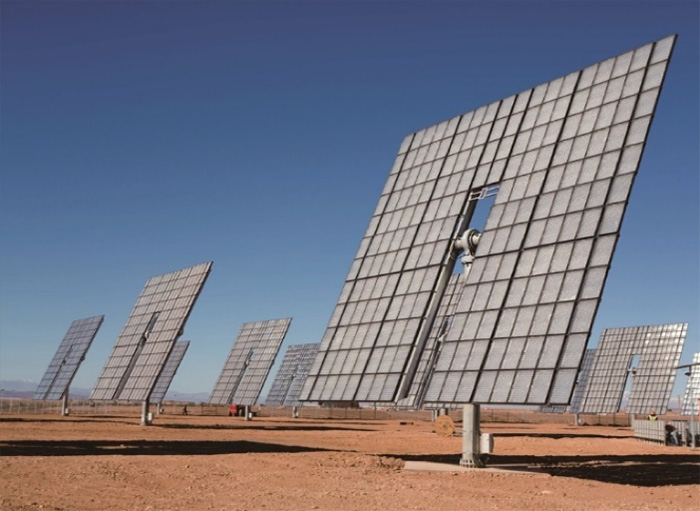
Since photovoltaic power generation does not generate carbon dioxide, it is known as a clean energy source that is useful for prevention of global warming, and it is a representative of renewable energy (renewable energy). The Paris Agreement, to which Japan is also a member, requires that carbon dioxide emissions be reduced in order to prevent global warming. Therefore, photovoltaic power generation is an important energy source that does not emit carbon dioxide. It is said that the energy payback time of ordinary photovoltaic power generation (one of the indicators of environmental friendliness by showing how many years the energy required to produce the equipment can be recovered by the energy generated by the equipment) is about 1 to 3 years, but the energy payback time is less than or equal because the power generation efficiency of CPV is more than twice as high as that of ordinary one. The lifetime is also about twice longer than that of ordinary photovoltaic power generation equipment, and is thought to be about 20 to 30 years. In other words, the ratio of the amount of energy produced in the lifetime of a photovoltaic generator to the amount of energy required in manufacturing is estimated to be approximately ten times that of a conventional photovoltaic generator, whereas the CPV is estimated to be approximately 20~25 times. Our goal is to realize more environmentally friendly power generation equipment by shortening the energy payback time and extending the life by increasing the power generation efficiency.
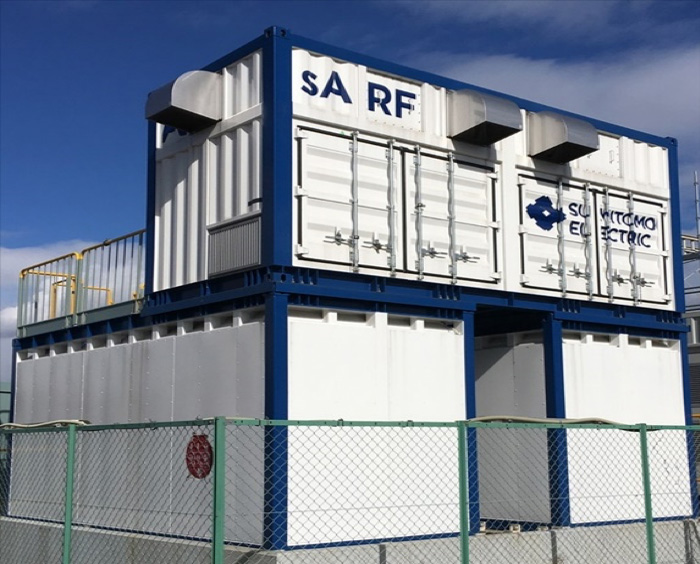
On the other hand, among renewable energy sources, photovoltaic power generation and wind power generation have weak points that depends on the weather and is difficult to control the amount of power generation. Large-scale storage batteries are expected to solve the problem of such re-energy instability. If this large-scale storage battery is connected to a renewable power generator or a backbone system, it can stabilize the system power by storing it when the power is surplus and discharging it when the power is insufficient. The storage battery for the electric power system is used by connecting to the electric power system in this way. The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry has supported demonstration experiments on storage batteries through the "Large-scale Power Storage System Emergency Demonstration Project" which has been promoted since 2013, the "Large-Capacity Power Storage System Demand-Supply Balance Demand Improvement Project" in 2015, and the "Large-scale Power Storage System Demand Balance Improvement Project" in 2016. Our redox flow batteries were also adopted in the large-scale storage system demonstration project conducted at the "Minami-Hayakita Substation" of Hokkaido Electric Power Co., Inc. Installation was completed in December 2015, with the aim of mitigating the effects of output fluctuations caused by renewable energy generation on power systems, and the company also aimed to establish optimum control and operation technologies to maximize the efficiency and life of system storage batteries. As a result, we were able to demonstrate that even when the output of re-energy changed rapidly, it could be smoothed by outputting the electricity stored in the storage battery. Usually, batteries use flammable metals such as lithium and sodium, which poses a fire risk. In contrast, redox flow batteries have zero fire risk because they do not use any combustible materials. Because the scale of the storage battery for the electric power system is large (the scale of the demonstration system of Hokkaido Electric Power Co., Inc. is 15,000 kW in output and 60,000 kWh in capacity), the feature that the risk of fire is zero is extremely important, and it is very safe for the environment. The redox flow battery is a storage battery that performs charging and discharging by utilizing the oxidation-reduction reaction of the ions of the chemical substances used for the electrolyte solution, and has many advantages that are environmentally friendly compared to other storage batteries, such as a long lifetime of the charging and discharging cycle and an ability to accurately monitor the state of charge even in an operating state. Thus, by using storage batteries for the electric power system, it is possible to improve the supply-demand balance of electric power or increase the amount of possible introduction of renewable energy. Our goal is to improve the performance of more environmentally friendly storage batteries for electric power systems and to develop an environment in which the introduction of renewable energy can be promoted with the aim of lowering the cost.
Other Innovation Challenges
Development and Dissemination of High-Temperature Superconducting Technology
Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd.
Similar Innovation Challenges
Accelarating the penetration of renewable energy resources with “Open Energy System”
Sony Group Corporation
Achieving net-zero carbon emissions from plant factories using full artificial lighting
Taikisha Ltd.
Advanced technology for buildings providing energy-saving and comfortable indoor environment (under Net Zero Energy condition)
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
AI control reduces base station power consumption by up to 50%
KDDI CORPORATION